FIGURE 5.
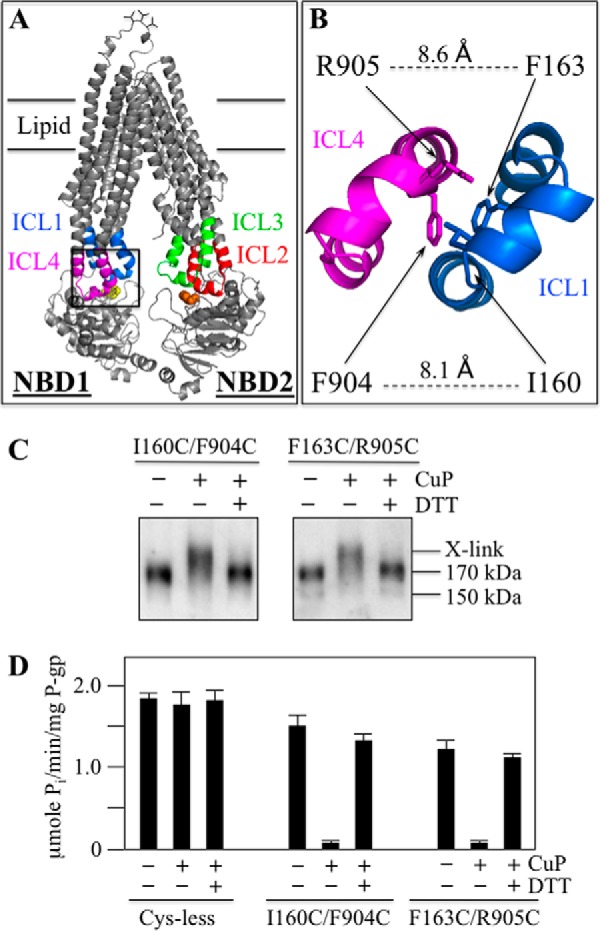
IH1/IH4 cross-linking inhibits P-gp ATPase activity. A, model of human P-gp showing parts of the various ICLs. The boxed inset is expanded in B to show the positions of residues I160C(IH1), F904C(IH4), F163C(IH1), and R905C(IH4). The distances (Å) between the α carbons of I160(IH1)/F904(IH4) and F163(IH1)/R905(IH4) are indicated. C, histidine-tagged Cys-less P-gp or mutants containing pairs of cysteines introduced into IH1 and IH4 (I160C(IH1)/F904C(IH4), F163C(IH1)/R905C(IH4)) (in Cys-less background) were transiently expressed in HEK 293 cells and isolated by nickel-chelate chromatography. Samples of the isolated P-gps were treated without (−) or with (+) copper phenanthroline (CuP). The reactions were stopped by addition of EDTA. Samples from the mutant P-gps were subjected to immunoblot analysis before (−) or after (+) treatment with dithiothreitol (DTT). The positions of cross-linked (X-link), mature (170 kDa), and immature (150 kDa) P-gps are indicated. D, samples were also assayed for ATPase activity in the presence of verapamil. Each value is the mean ± S.D. (n = 3).
