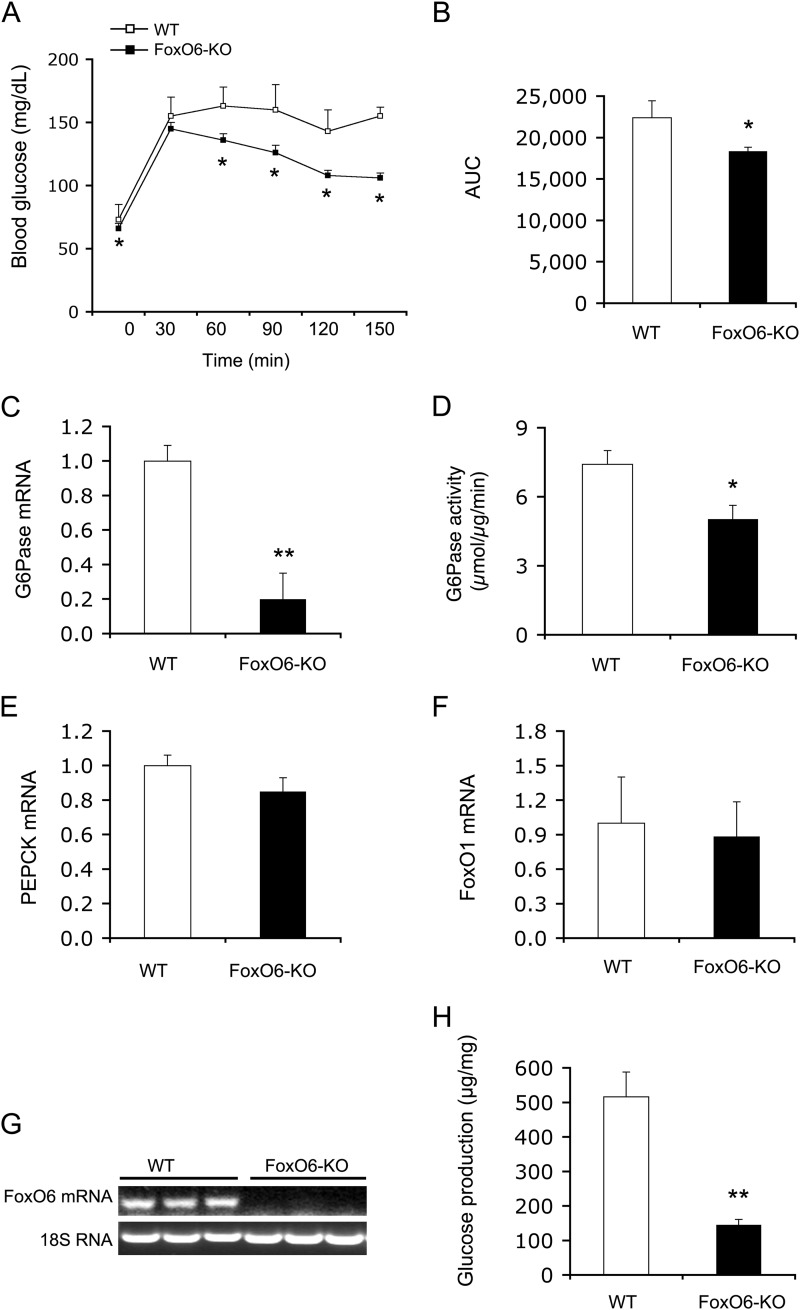
FIGURE 2.
Effect of FoxO6 deletion on hepatic gluconeogenesis. A, pyruvate tolerance test. B, AUC. The AUC was calculated from blood glucose profiles during pyruvate tolerance test. C, G6Pase mRNA levels. D, hepatic G6Pase activity. E, PEPCK mRNA levels. F, FoxO1 mRNA levels. G, hepatic FoxO6 mRNA. Mice were sacrificed after 16-h fasting. Liver tissues were used for isolating total RNA, which was subjected to real-time qRT-PCR analysis. Hepatic G6Pase, PEPCK, FoxO1, and FoxO6 mRNA levels were determined using 18S RNA as control. Aliquots of liver tissues (40 mg) were used for the preparation of microsomes, which were subjected to G6Pase activity assay for determining hepatic G6Pase activity, defined as the production of Pi (in μmole) per unit time (in minutes) per μg of cellular microsomes. H, glucose production in mouse primary hepatocytes. Mouse primary hepatocytes of FoxO6-KO and WT mice were cultured in the absence or presence of 8-cpt-cAMP (cAMP analog, 500 μm) and dexamethasone (100 μm). Each condition was run in six replicates. After 24-h of incubation, the amount of glucose released from hepatocytes into culture medium was determined. Data in panels A–G were obtained from male FoxO6-KO mice (n = 14) and age/sex-matched WT littermates (n = 7) on regular chow at 4 months of age. p < 0.05 (*) and p < 0.001 (**) versus WT control.