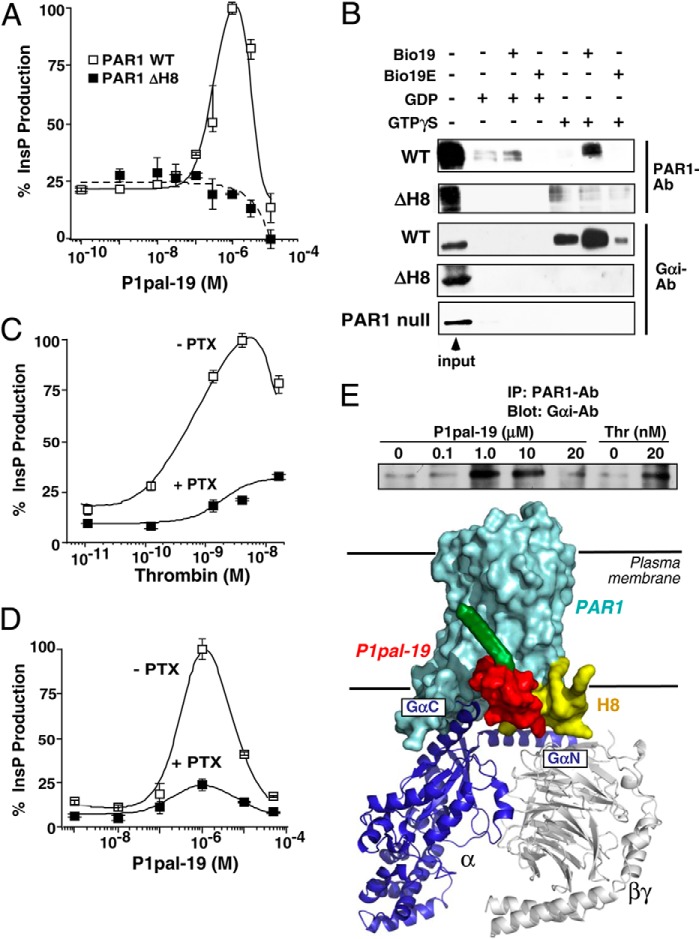
FIGURE 3.
The i3 loop peptide directly interacts with the PAR1 H8 helix region. A, deletion of the PAR1 H8 helix causes complete loss of the receptor-PLC-β (InsP) response to P1pal-19 in COS7 cells. B, binding of WT PAR1 or ΔH8 PAR1 and Gαi to avidin-N-biotin-i3 loop peptides. HEK293 cells were transfected with WT PAR1 or ΔH8, or PAR1-null Rat 1 cells were used. Membrane lysates were incubated with avidin beads that were precoated with the biotinylated WT i3 loop peptide (Bio19) or negative control i3 loop (Bio19E) in the presence of 10 μm GDP or GTPγS. Eluted proteins were resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE, and Western blotting was performed to detect PAR1 (SFLLR-Ab; 1:500) or Gαi (Gαi1/2-Ab; 1:1000). C and D, Gαi inhibitor pertussis toxin (PTX) suppresses PAR1-PLC-β activity of PAR1 Rat 1 cells stimulated by either thrombin or P1pal-19. E, top, P1pal-19 and thrombin enhance binding of Gαi to PAR1. PAR1 Rat 1 cells were stimulated for 10 min with P1pal-19 or thrombin (Thr). Cell lysates were then incubated with PAR1-Ab-coated protein A beads, and bound Gαi protein was detected by Western blotting. Bottom, schematic representation of the PAR1·G protein complex bound to P1pal-19. Error bars represent S.D. IP, immunoprecipitation.