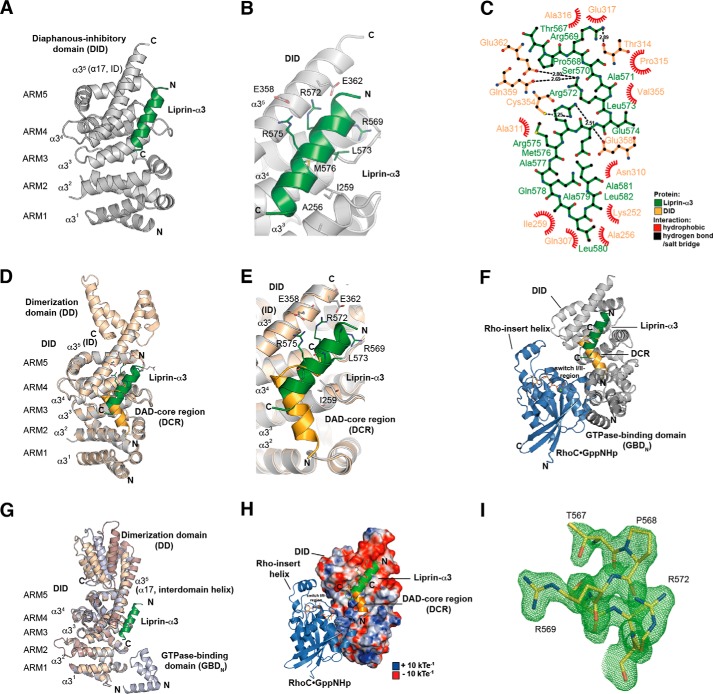
FIGURE 2.
Structure of the Lip(567–587)·DID complex. A, ribbon representation of the Lip(567–587)·DID (aa 135–369) complex (left) and a 90° clockwise rotated view (right). Liprin-α3 (green) binds to the ARM3 to -5 region of DID (gray) in an orientation antiparallel to ID α17. B, close-up of the Lip(567–587)·DID structure. Liprin-α3 makes electrostatic interactions with the ID (Arg-575L–Glu-358D and Arg-572L–Glu-362D) as well as hydrophobic interactions using Leu-573L, Met-576L, and other residues. C, schematic presentation of the interactions in the Lip(567–587)·DID structure generated with LigPlot+ version 1.4.5. Liprin-α3 makes hydrophobic as well as specificity-creating salt bridges with the mDia1 DID. D, superposition of the Lip(567–587)·DID (gray/green) structure with the mDiaNΔG·DAD (light orange/dark orange) structure (PDB code 2BAP). The liprin-α3 and DAD-binding sites overlap significantly. E, detailed view of the superposition of Lip(567–587)·DID and mDiaNΔG·DAD. The C-terminal half of liprin-α3 overlaps with the C-terminal half of the DCR. Liprin-α3 follows the path of the DBR along the mDiaN ID. F, composition of the putative ternary complexes of liprin-α3·RhoC·mDiaN (green/blue/gray; PDB code 2BAP) and liprin-α3·DAD·DID (green/orange/gray; PDB code 1Z2C). The subdomain GBDN from the RhoC·mDiaN (PDB code 1Z2C) structure is shown in dark gray. RhoC does not make any obvious steric or electrostatic clashes with liprin-α3. G, structural similarity of DID from the complexes of RhoC·mDiaN (PDB code 1Z2C), DAD·mDiaNΔG (PDB code 2BAP), mDiaN (PDB code 2BNX), and Lip(567–587)·DID. The mDiaN fragments shown were superposed on the DID. The structures are highly similar in the DID with root mean square deviation values ranging from 0.401 to 0.583 Å for the peptide backbone and from 0.367 to 0.541 Å for the Cα atoms. Structural differences are only visible in the ID and the following DD (aa 369–451) not present in the structure presented here. Lip(567–587)·DID resembles most the uncomplexed mDiaN structure (PDB code 2BNX). H, electrostatic surface potential of DID as generated by APBS. RhoC, DAD, and liprin-α3 are shown as they are located on the mDiaN surface. RhoC uses switch I and II to interact with a positively charged groove on the DID surface. As a second binding site, the Rho insert helix is within interaction distance to the ARM4/5 of the DID. Lip(567–587) is located along ID α17 connecting the DID and the DD of mDiaN. Arg-572L and Arg-575L make salt bridges toward negatively charged residues Glu-362D and Glu-358D of the mDiaN ID. The C-terminal part of the ID is highly negatively charged. Blue, positive charge; red, negative charge. The figure is scaled from −10 to +10 kbTeC−1 (kb, Boltzmann's constant; T, temperature in Kelvin; eC−1, elementary charge). I, FO − FC omit difference map of the N-terminal part of the liprin-α3 peptide covering residues Thr-567 to Arg-572 (chain D) countered at 3σ.