FIGURE 7.
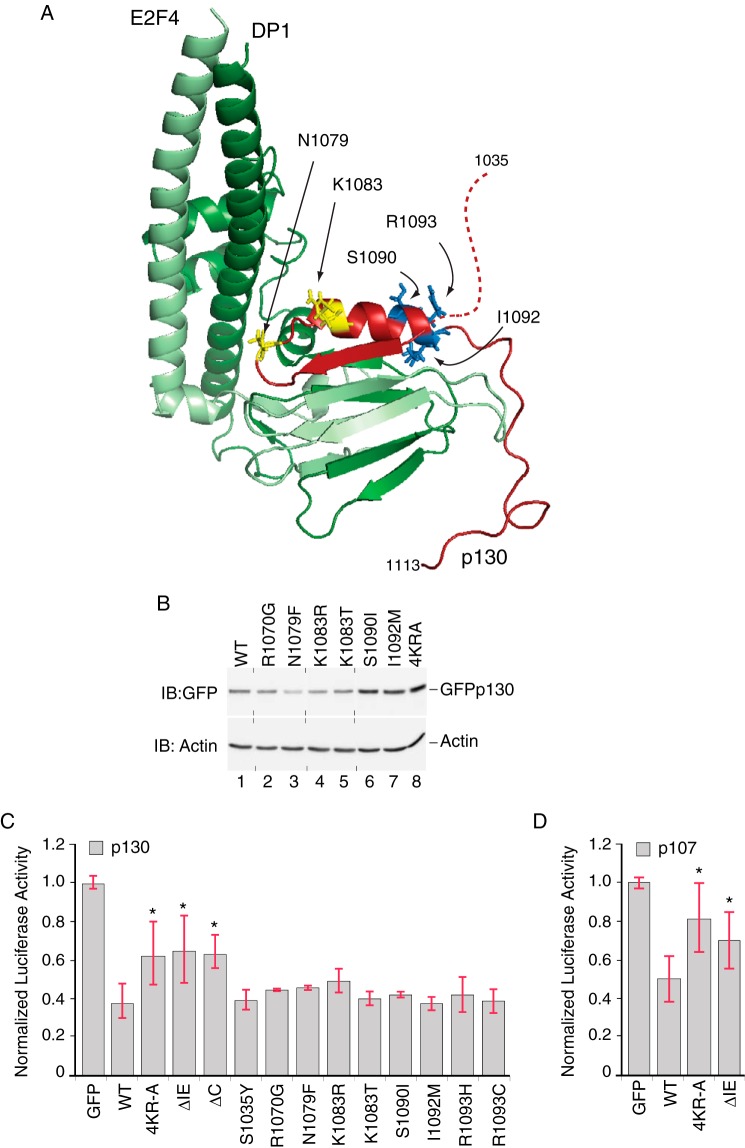
p130 IE activity in repressor potency and stability are biochemically separable functions. A, model of the human p130 IE in a complex with E2F4-DP1. Homology model of the p130 C terminus (residues 1035–1113, red) in complex with the coiled coil-marked box domains from E2F4 (residues 94–198, light green) and DP1 (residues 199–350, dark green) was generated using the crystal structure of the RB C-terminal domain bound to an E2F1-DP1 heterodimer as an template (PDB code 2AZE; Ref. 40). The N-terminal portion of the p130 IE is unstructured in this model (dashed red line), whereas the C-terminal portion of the IE harbors a sheet (residues 1071–1077)-turn-helix (1083–1093) motif. The positions of some amino acid residues altered in human cancer patients are indicated (documented in COSMIC-S1090I, TCGA-23-1118-01; I1092M, TCGA-AA-3864-01; R1093H, TCGA-AA-A01Q-01; R1093C, TCGA-D1-A15W-01A-11D-A122-09). In all cases, these mutations are rare, occurring at a frequency if ≤0.3%. Additional mutants (R1070G, 2/14 cases; N1079F, 2/14 cases; K1083R, 4/14 cases; K1083T, 1/14 cases) are based on the study presented in Ref. 53. Residues highlighted in yellow (Asn-1079, Lys-1083) are located toward the N-terminal region of the α-helix, whereas residues highlighted in blue (Ser-1090, Ile-1092, Arg-1093) are located within the C-terminal region of this helix. B, cancer-associated IE mutations have variable effects on p130 levels. Anti-GFP Western blot (IB) analysis was performed on U2OS cells transfected with plasmids expressing either wild type GFP-p130 or mutant versions harboring single point substitutions, as indicated. In two replicates, GFP-130 containing the S1090I and I1092M substitutions was expressed 2.2- and 1.7-fold greater than the wild type (n = 2). Vertical dashed lines indicate positions where the image had been cut to rearrange the order of lanes. C, the p130 IE is required for full repression potency. Luciferase reporter assays were performed in the presence of wild type or mutant versions of GFP-130, as indicated, testing repression of the human CCNA2 luciferase reporter. Wild type GFP-p130 repressed transcription by 63% as compared with GFP alone. GFP-p1304KR-A, GFP-p130ΔIE, and GFP-p130ΔC were significantly less effective than wild type GFP-p130 (n = 8; *, p < 0.05). None of the IE mutations reported in human cancers statistically altered the repression of CCNA2 reporter by GFP-p130. D, the p107 IE is required for full repression potency. Luciferase reporter assays were performed in the presence of wild type or mutant versions of GFP-107, as indicated, testing repression of the human CCNA2 luciferase reporter. Wild GFP-p107 repressed transcription by 50% as compared with GFP alone. Both GFP-p1074KR-A and GFP-p107ΔIE were significantly less effective than wild type GFP-p107 (n = 5; *, p < 0.05).