FIGURE 6.
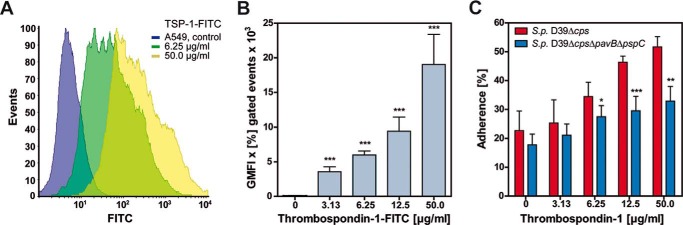
PavB and PspC contribute to pneumococcal adherence to A549 cells via hTSP-1. A and B, dose-dependent binding of hTSP-1-FITC to A549 cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. Approximately 2 × 105 cells were incubated with different concentrations of FITC labeled hTSP-1 (0–50 μg/ml) after preincubation with 1 μm MnCl2. Binding of hTSP-1 is shown as a histogram and geometric mean fluorescence intensity (GMFI) multiplied by the percentage of gated events (GMFI × % gated events). The mean values of three independent experiments are shown with error bars corresponding to S.D. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. C, A549 cells (2 × 105) were preincubated with 1 μm MnCl2 and increasing concentrations of hTSP-1 followed by an infection with S. pneumoniae D39Δcps or D39ΔcpsΔpavBΔpspC using a multiplicity of infection of 25 bacteria per epithelial cell. Adherent bacteria were detected using a polyclonal rabbit anti-pneumococci antibody followed by incubation with secondary AlexaFluor® 488-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG. A549 cells were stained with AlexaFluor® 488-coupled phalloidin. Pneumococcal adherence of 100 cells was quantified 1.5 h post infection by immune fluorescence microscopy. Results are presented as percentage related to the multiplicity of infection for three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 versus S. pneumoniae D39Δcps.
