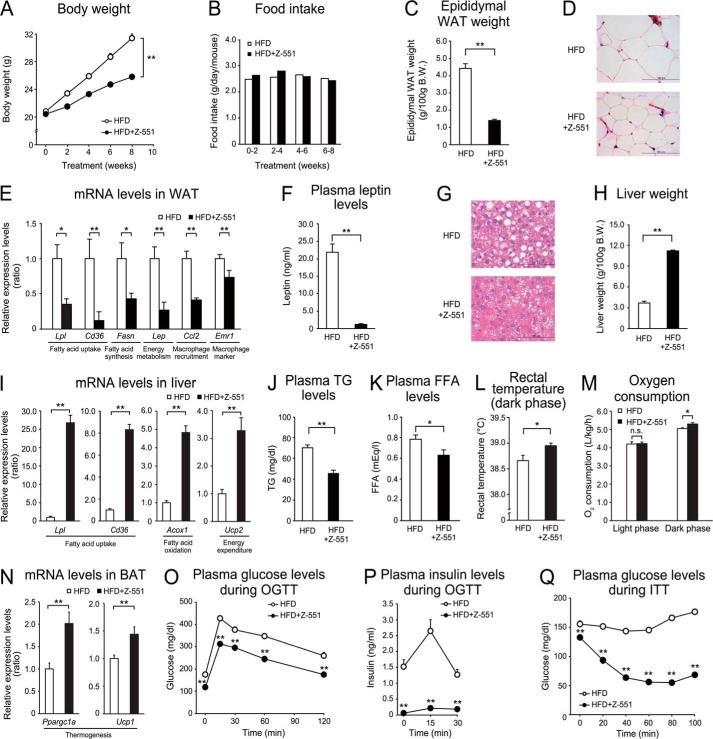
FIGURE 2.
Z-551 indicates preventive effects on diet-induced obesity and metabolic disorders in WT mice. 4-week-old male WT mice were acclimatized to the HFD for 1 week followed by administration of Z-551 for 9 weeks. A–C, changes in body weight (A), food intake (B), and epididymal WAT weight (C) in WT mice on the HFD (white) or HFD+Z-551 (black). D, morphology of epididymal WAT. Scale bars indicate 100 μm. E, mRNA expression levels in epididymal WAT. F, plasma leptin Week 8 after Z-551 administration. G, morphology of liver. Scale bars indicate 100 μm. H, liver weight, I, mRNA expression levels in the liver. J and K, plasma TG (J) and FFA (K) Week 4 after Z-551 administration. L, rectal temperature. Rectal temperature was measured during the dark phase Week 9 after Z-551 administration. M, oxygen consumption. Oxygen consumption was measured Week 3 after Z-551 administration. N, mRNA expression levels in BAT. O and P, plasma glucose (O) and insulin (P) in the OGTT Week 5 after Z-551 administration. Q, plasma glucose in the ITT Week 8 after Z-551 administration. In the OGTT, glucose (1.0 g/kg body weight (BW)) was orally administered after 6-h fasting. In the ITT, insulin (0.75 unit/kg BW) was intraperitoneally injected. Blood samples were obtained at the indicated times. All results are expressed as mean ± S.E. (n = 7–10). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; n.s., not significant.