FIGURE 10.
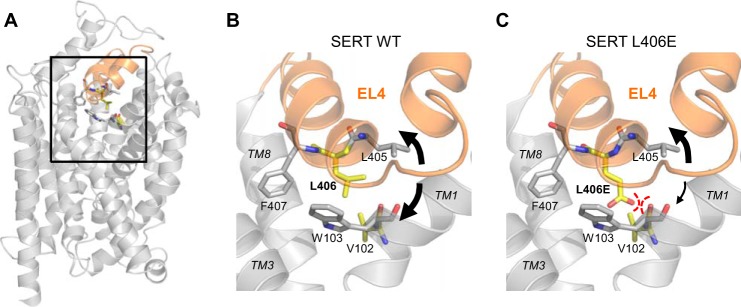
Putative interaction between L406E and a backbone carbonyl on TM1. A, location of EL4 (shown in orange) depicted on a homology model of SERT (9). B, close-up view of the EL4 (boxed area in A) and the surrounding TMs (TM 1, 3, and 8). Val-102 (TM1) and Leu-406 (EL4) are shown as yellow sticks, and Trp-103 (TM1) and Phe-407 (EL4) are shown as gray sticks. The presumed flexibility of EL4 is indicated by black arrows. C, the L406E mutation was constructed using PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, version 1.3 (Schrödinger, LLC) using its backbone-dependent rotamer library. The close proximity between the negatively charged carboxylate group on the side chain of L406E and the backbone carbonyl group of Val-102 could possibly induce a repulsive interaction that would restrict the flexibility of EL4 and TM1.
