FIGURE 1.
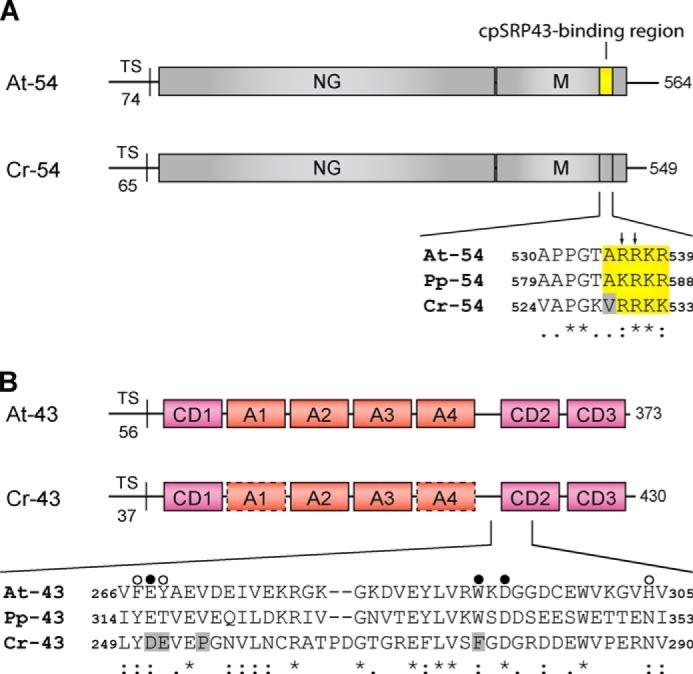
Domain organization of the cpSRP54 and cpSRP43 proteins and sequence alignment of the binding regions. A, cpSRP54 consists of an N-terminal GTPase-containing domain (NG) and a C-terminal methionine-rich domain (M). The sequence alignment shows the cpSRP43-binding motif of A. thaliana cpSRP54 (At-54) and the corresponding regions in cpSRP54 of P. patens (Pp-54) and C. reinhardtii (Cr-54). The conserved residues that are important for binding are depicted in yellow. Arrows indicate the twin arginine motif (Arg-536/Arg-537) that is crucial for cpSRP43 binding in Arabidopsis. The gray box indicates Val-529 in Cr-cpSRP54 that interferes with cpSRP43 binding. TS, transit sequence. B, cpSRP43 consists of three chromodomains (CD1–CD3) and an ankyrin repeat domain (A1–A4). The sequence alignment shows the region of CD2 composed of the twinned cages that recognize Arg-536 and Arg-537 in At-cpSRP54 (16). The cage 1- and cage 2-forming residues of At-cpSRP43 and the corresponding positions in Pp-cpSRP43 (Pp-43) and Cr-cpSRP43 (Cr-43) are marked with filled and open circles, respectively. The gray boxes indicate residues in Cr-cpSRP43 that differ in these positions from At-cpSRP43 (At-43) and Pp-cpSRP43. In addition, Pro-255 in Cr-cpSRP43 that interferes with cpSRP54 binding is marked by a gray box. Symbols display the degree of conservation: identical residues (asterisk), conserved substitution (colon), semiconserved substitution (dot).
