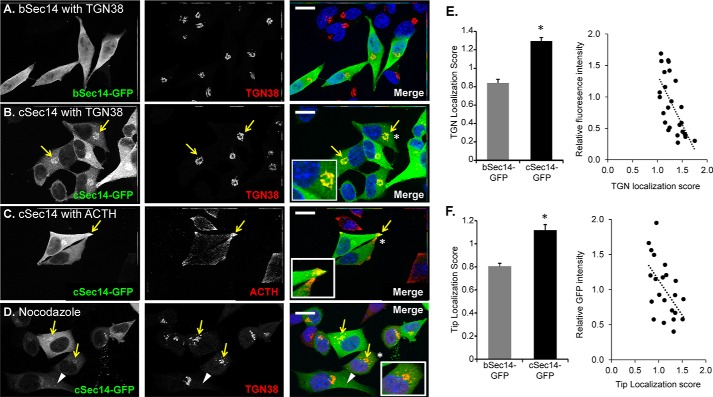
FIGURE 4.
Differential localization of bSec14- and cSec14-GFP in AtT-20 cells. Immunostaining of AtT-20 cells transiently transfected with vectors encoding bSec14-GFP or cSec14-GFP revealed that bSec14-GFP was diffusely localized (A), whereas cSec14-GFP co-localized with the TGN marker, TGN38 (B; yellow arrows) and with ACTH (C; yellow arrows), a marker for the mature secretory granules that accumulate at the tips of cellular processes. Insets, higher magnification of areas marked by white asterisks. D, cells were treated with a low dose of nocodazole (10 μm) for a short time (30 min) to disrupt the microtubule-dependent trafficking of late/recycling endosomes into the perinuclear region (38). Much of the cSec14-GFP continued to co-localize with TGN38 (yellow arrows), but some cSec14-GFP-positive vesicular structures that lacked TGN38 could be identified (white arrowheads). The merged images show GFP in green, and TGN38 (A, B, and D) or ACTH (C) in red, and Hoechst in blue. Scale bar, 20 μm. E and F, quantification of Sec14-GFP localization. Localization scores were calculated by taking the ratio of GFP signal intensity in the indicated area (TGN or tips) over cytosolic signal intensity. For TGN localization, n = 18 and 25 cells for bSec14- and cSec14-GFP, respectively. For localization to tips, n = 26 and 22 cells for bSec14- and cSec14-GFP, respectively. For both parameters, localization scores for cSec14-GFP were inversely related to relative GFP intensity; least squares best fit lines are shown. Both localization scores (TGN and tip) differ for cSec14-GFP and bSec14-GFP; p < 0.001 (Student's t test). Error bars, S.E.