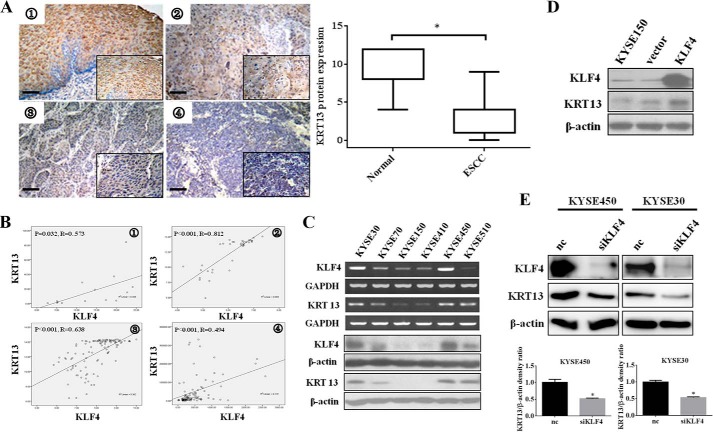
FIGURE 2.
Expression of KRT13 and KLF4 are correlated in esophageal squamous carcinoma cell lines and tissues. A, representative images of KRT13 staining are shown in normal esophageal epithelium ➀, well differentiated ➁, moderately differentiated ➂, and poorly differentiated ➃ carcinoma tissue sections (bar, 15 μm). Quantitative analysis of the KRT13 staining between ESCC tissues and the matched normal esophageal epithelia are shown on the right. B, statistically significant positive correlation between klf4 and KRT13 mRNA was observed by Pearson's method in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines and tissues in four independent published data sets (➀ GSE9982, ➁ GSE21293, ➂ GSE23400, and ➃ GSE33103). C, expression of KLF4 and KRT13 in a series of esophageal cancer cell lines was determined by RT-PCR (upper panel) and Western blot analysis (lower panel). D, KYSE150 cells were transiently transfected with the pcDNA3.1 and pcDNA3.1-KLF4 vector; cells were harvested, and Western blot was performed to measure the protein expression of KLF4 and KRT13. E, Western blot analysis showed the protein expression of KLF4 and KRT13 in KYSE30 and KYSE450 cells transfected with KLF4 siRNA pools (si-KLF4) or nontargeting control (nc). β-Actin serves as an internal control. The band intensities of KRT13 protein were quantified by densitometry and normalized against β-actin. The data represent the means ± S.D. *, p < 0.05.