FIGURE 2.
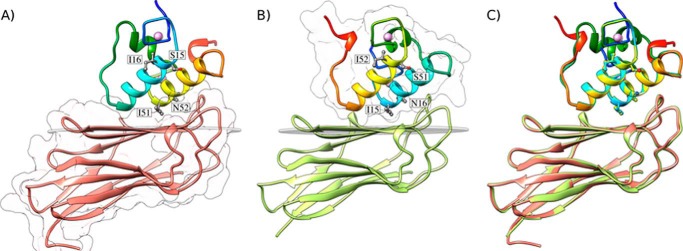
Structures of the A. cellulolyticus cohesin-dockerin complexes. A, structure of Coh_DocI15S/N16I with the dockerin color-ramped from N terminus (blue) to C terminus (red) and the cohesin in salmon. Ile-51 and Asn-52 that dominate cohesin recognition and engineered residues Ser-15 and Ile-16, to force a single binding mode, are labeled and shown as ball-and-stick configuration. Ca2+ ions are depicted as purple spheres. B, structure of Coh_DocI51S/N52I with the dockerin color-ramped from N terminus (blue) to C terminus (red) and the cohesin in green. Ile-15 and Asn-16 that dominate cohesin recognition and engineered residues Ser-51 and Ile-52, to force a single binding mode, are again labeled and shown as ball-and-stick representations. C, overlay of the two binding modes showing the high degree of overall similarity reflecting the internal 2-fold symmetry of the dockerin module. The transparent gray disk in A and B marks the plane defined by β-sheet B, and the β-strands form a distinctive dockerin interacting plateau. A and B also depict a representation of the molecular surface contour of the cohesin and dockerin, respectively.
