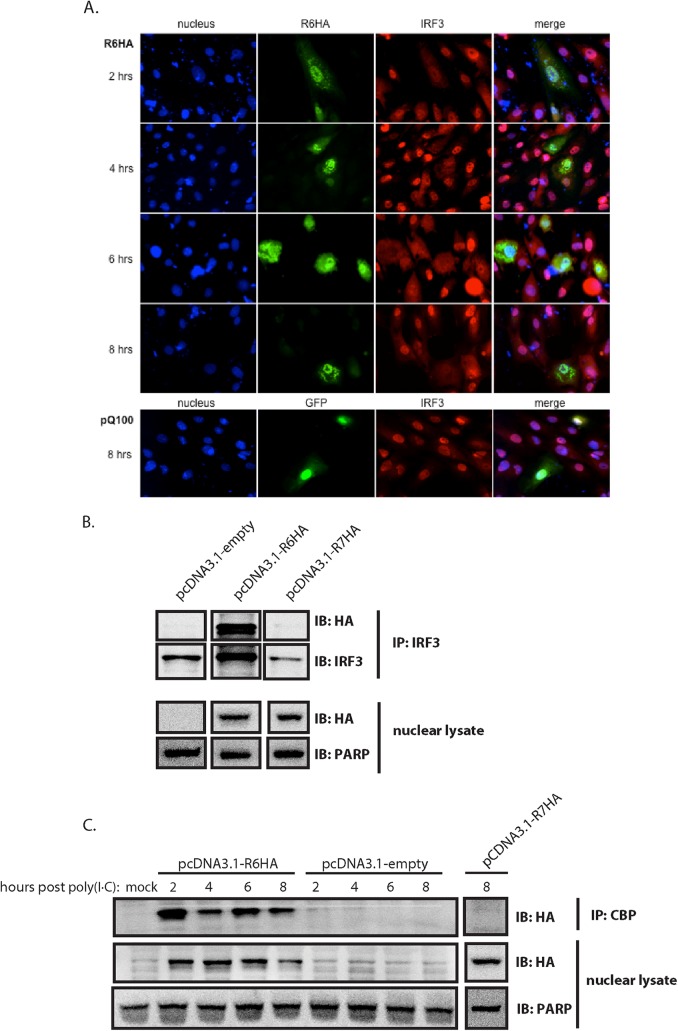
FIG 2.
R6 localizes to the nucleus and affects nuclear accumulation of pIRF3. (A, B, and C) Telomerized RFs were transfected with pcDNA3.1-R6HA, pcDNA3.1-R7HA, or empty pcDNA3.1 for 40 h and subsequently transfected with poly(I · C) for the indicated times. (A) Transfected cells were fixed and analyzed by immunofluorescence for the detection of R6 (anti-HA) (green) and cellular IRF3 (red) and stained with Hoechst (blue) for the detection of nuclei. (B) Nuclear lysates prepared from cells 8 h post-poly(I · C) transfection were immunoprecipitated with anti-IRF3 antibody and then subjected to SDS-PAGE and probed with anti-HA antibody. Nuclear lysates were probed for HA expression, with PARP as a loading control and as a control for purity of nuclear fractionation. IB, immunoblotting. (C) Nuclear lysates were immunoprecipitated with CBP antibody and then subjected to SDS-PAGE and probed with anti-HA antibody. The nuclear lysates were probed for HA expression, with PARP as a loading control and as a control for purity of nuclear fractionation.