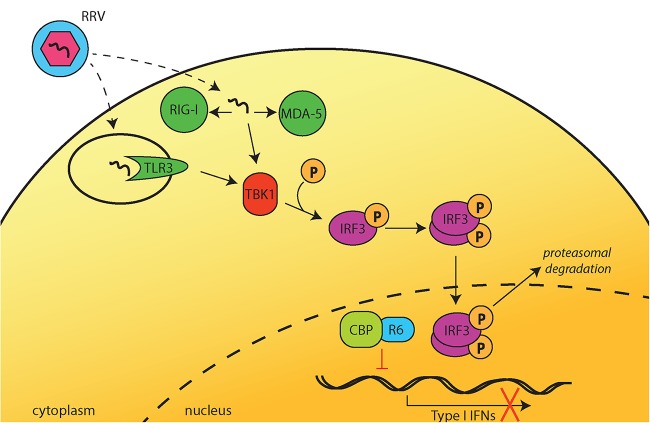
FIG 7.
Potential model of IFN inhibition by R6. Upon detection of RRV infection by TLR3, RIG-I, or MDA-5, TBK1 is activated and subsequently phosphorylates IRF3. pIRF3 then dimerizes and translocates to the nucleus. Within the nucleus, R6 binds to the transcriptional coactivator CBP. This interaction prevents pIRF3 from binding to CBP, and pIRF3 is exported from the nucleus and degraded by the proteasome. Nuclear R6 interferes with complex formation between pIRF3 and CBP and, as a result, decreases pIRF3/CBP complex binding to the IFN-β promoter and inhibits IFN-β production.