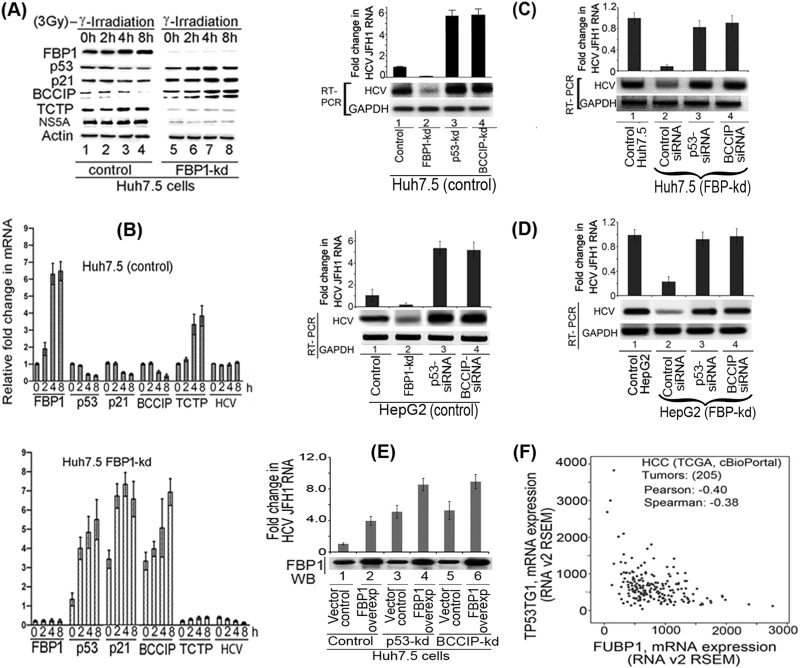
FIG 7.
FBP1 promotes HCV replication by regulating p53 and its regulatory proteins, TCTP and BCCIP. (A) FBP1 upregulates TCTP while it downregulates the expression of p53, p21, and BCCIP under cellular stress. The control and FBP1-kd Huh7.5 cells were transfected with JFH1-HCV virus; 72 h later, cells were irradiated with 3 Gy gamma irradiation and grown for the indicated times, and their cell lysates were examined for the expression of FBP1, p53, p21, BCCIP, TCTP, and NS5A by Western blotting. Lanes 1 to 4 (control Huh7.5 cells) and lanes 5 to 8 (FBP1-kd Huh7.5 cells) show results after growth for 0, 2, 4, and 8 h postirradiation. (B) Fold change in HCV RNA and mRNA level of FBP1, p53, p21, BCCIP, and TCTP in control (top) and FBP1-kd (bottom) Huh7.5 cells. Quantitative RT-PCR on total RNA isolated from another set of cells in the same experiment was done to determine relative fold changes in mRNA levels of FBP1, p53, p21, BCCIP, TCTP, and HCV RNA at 0, 2, 4, and 8 h postirradiation. (C, left) Control Huh7.5 cells knocked down for either p53Y220C or BCCIP are highly permissive to HCV replication. Lane 1, control cells; lane 2, FBP1-kd cells; lane 3, p53-kd cells; lane 4, BCCIP-kd cells. (Right) HCV replication in FBP1-kd Huh7.5 cells is restored by downregulation of either p53 or BCCIP. Lane 1, untransfected control Huh7.5 cells; lanes 2 to 4, FBP1-kd cells were transfected with control siRNA, p53-siRNA, and BCCIP-siRNA, respectively. (D, left) Downregulation of p53 or BCCIP enhances HCV replication in control HepG2/CD81/miR122 cells. HepG2 cells expressing CD81 and miR122 were transfected with either p53 siRNA or BCCIP siRNA, and 12 h later they were infected with JFH1 HCV virions. Cells were grown for 72 h and analyzed for HCV RNA level by quantitative real-time PCR. Lane 1, control cells; lane 2, FBP1-kd cells; lanes 3 and 4, cells transfected with p53-siRNA and BCCIP-siRNA, respectively. (Right) Downregulation of p53 or BCCIP restored HCV replication in FBP1-kd HepG2/CD81/miR122 cells. FBP1-kd HepG2 cells expressing CD81 and miR122 were transfected with p53-siRNA or BCCIP-siRNA. After 12 h posttransfection, cells were infected with JFH1 HCV and grown for 72 h. Total RNA was isolated, and quantitative real-time PCR determined the level of HCV RNA. Lane 1, untransfected control HepG2 cells; lanes 2 to 4, FBP1-kd cells were transfected with control siRNA, p53-siRNA, and BCCIP-siRNA, respectively. (E) The level of HCV replication in highly permissive p53-kd or BCCIP-kd cells is further increased by overexpression (overexp) of FBP1. The FBP1 overexpression plasmid (pCIA-CMV-FBP) was transfected into control, p53-kd, and BCCIP-kd Huh7.5 cells; 10 h later cells were infected with HCV-JFH1 virions. The cells transfected with vector alone were used as controls. The cells were grown for 72 h, and levels of HCV RNA were determined by quantitative RT-PCR. The FBP1 expression in cells was examined by Western blotting of the normalized cell lysates. Lanes 2, 4, and 6 are control, p53-kd, and BCCIP-kd cells, respectively, in which FBP1 was overexpressed. Lanes 1, 3, and 5 are the respective vector controls. (F) The cBioPortal coexpression analysis of FBP1 and p53-inducible gene TP53TG1. The cBioPortal coexpression analysis was done on data from 205 HCC tumors (TCGA, Provisional), indicating an inverse correlation between the expression of FBP1 and the p53-inducible gene, TP53TG1.