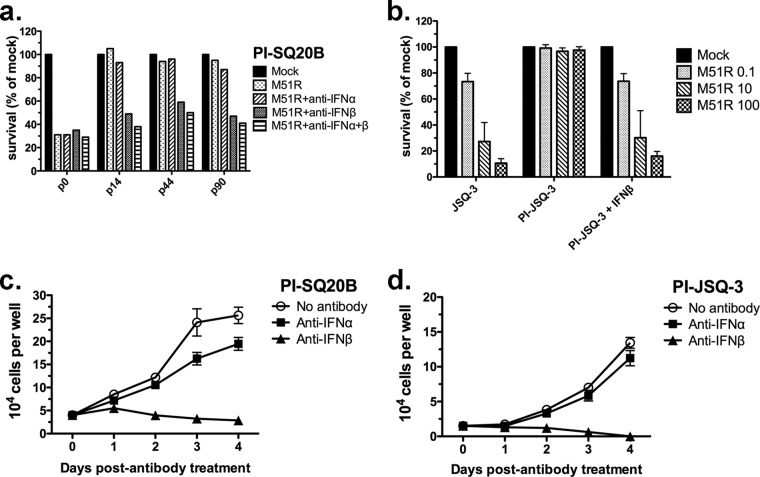
FIG 6.
IFN-β maintains the state of persistent infection in tumor cells. (a) SQ20B cells that had established persistent M51R VSV infections (PI-SQ20B) were reinfected at the indicated passage (p) number with M51R VSV at an MOI of 0.1. p0 indicates cells that were infected for the first time (not persistently infected). Neutralizing antibodies to IFN-α, IFN-β, or a combination of the two antibodies were added to some cultures 18 h prior to the addition of virus. At 48 h after reinfection with M51R VSV at the indicated MOI, viability was measured by MTT assay. Results are expressed as the percentage of cells, relative to the number of mock-infected cells, that survived reinfection. Three passages are shown. The results from all three passages were pooled for analysis of variance. The following survival differences (P < 0.05) were found for the treatment groups: (i) anti-IFN-β and anti-IFN-α plus anti-IFN-β groups had decreased survival relative to the no-antibody groups, and (ii) anti-IFN-β groups had decreased survival relative to the anti-IFN-α groups. (b) Persistently infected JSQ-3 cells were maintained continuously in the presence of exogenous IFN-β. When virus was no longer detectable in the cultures, the cells were reinfected with M51R VSV and viability was measured 48 h later. Persistently infected SQ20B (PI-SQ20B) (c) or JSQ-3 (PI-JSQ-3) (d) cells were treated with neutralizing anti-IFN-β or anti-IFN-α antibodies, and viability was measured over 4 days. The number of viable cells per well was determined by light microscopy using the criteria of trypan blue exclusion. The means ± SD from 3 determinations per time point are shown. The following survival differences (P < 0.05) at day 4 were found: (i) the no-antibody group survived in greater numbers than the anti-IFN-β group, and the anti-IFN-α group survived in greater numbers than the anti-IFN-β group for both cell lines. (c and d) Differences in group-by-time interaction (slope) (P < 0.05) were the following: the no-antibody group survived in greater numbers than the anti-IFN-α group, which survived in greater numbers than the anti-IFN-β group (c); the no-antibody group survived in greater numbers than the anti-IFN-β group, and the anti-IFN-α group survived in greater numbers than the anti-IFN-β group (d).