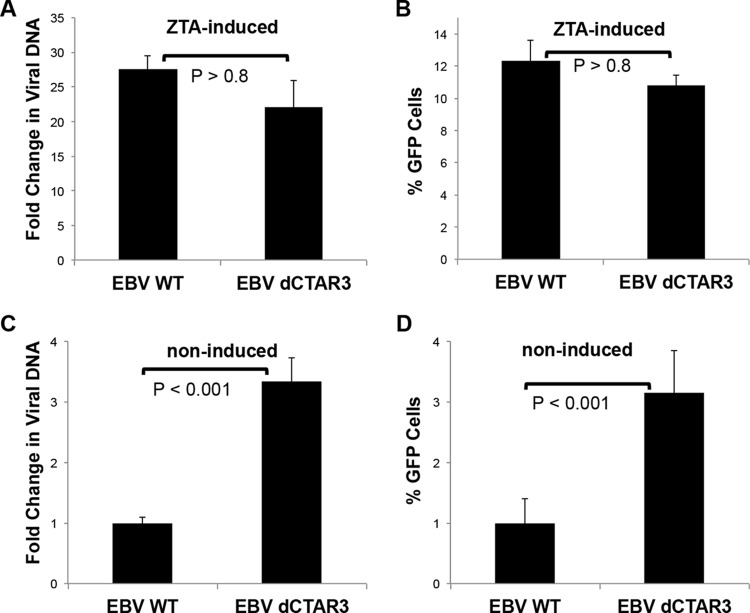
FIG 1.
Deletion of CTAR3 did not affect viral replication but increased background levels of lytic replication. EBV WT- and EBV dCTAR3-expressing 293 cells were induced by transfection with ZTA expression plasmids or noninduced by transfection with the vector control, and cells and supernatants were collected at 48 h posttransfection. (A) Virus was harvested, and relative viral loads were quantitated by real-time PCR. The fold change in the amount of viral DNA (relative to that for noninduced EBV WT- and EBV dCTAR3-expressing 293 cells) was determined. (B) Raji cells were exposed to the remaining supernatants. The percentages of GFP-positive cells were determined by flow cytometry after 48 h. (C) For noninduced cells, the fold change in the amount of viral DNA (relative to that for noninduced EBV WT-expressing 293 cells) was determined. (D) Raji cells were exposed to the remaining supernatants. The percentages of GFP-positive cells were determined as described above. Results are shown as means ± standard deviations from experiments performed in triplicate.