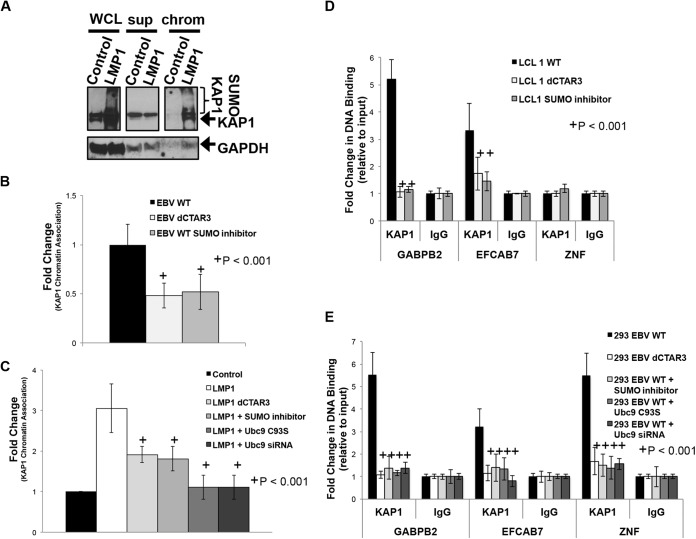
FIG 6.
LMP1 CTAR3-induced sumoylation regulates KAP1 function. (A) Whole-cell lysates, chromatin-enriched extracts (chrom), and the corresponding supernatants (sup) collected from 293 cells transfected with LMP1 expression constructs or control expression constructs; (B) paired EBV WT- and EBV dCTAR3-transformed LCLs and EBV WT-transformed LCLs treated with SUMO inhibitors (25 μM anacardic acid and 25 μM ginkgolic acid); (C) 293 cells transfected with a vector control expression construct and scrambled siRNA, LMP1 dCTAR3 expression constructs, LMP1 expression constructs, LMP1 expression constructs treated with SUMO inhibitors (25 μM anacardic acid and 25 μM ginkgolic acid), LMP1 and Ubc9 C93S expression constructs, and LMP1 expression constructs treated with Ubc9 siRNA. (A) Western blot analyses were performed, and KAP1 and GAPDH levels were detected. (B and C) Densitometric analysis of repeat immunoblots and slot blot analyses were performed, and the KAP1 levels in chromatin fractions relative to the levels in whole-cell lysates were determined. Fold changes in KAP1 chromatin association were determined. (D and E) Paired EBV WT- and EBV dCTAR3-transformed LCLs and EBV WT-transformed LCLs treated with SUMO inhibitors (25 μM anacardic acid and 25 μM ginkgolic acid) (D) and EBV WT-expressing 293 cells, EBV dCTAR3-expressing 293 cells, and EBV WT-expressing 293 cells treated with SUMO inhibitors (25 μM anacardic acid and 25 μM ginkgolic acid), transfected with Ubc9 C93S-expression constructs, or transfected with Ubc9 siRNA (E) were grown, and chromatin immunoprecipitations were performed with KAP1-specific antibodies or control IgG antibodies. Real-time PCR analyses were performed to examine the KAP1 association with the GABPB2, EFCAB7, and ZNF gene promoters. The fold change in DNA binding (relative to that for the input controls) was determined. Results are shown as means ± standard deviations from experiments performed in triplicate.