FIG 3.
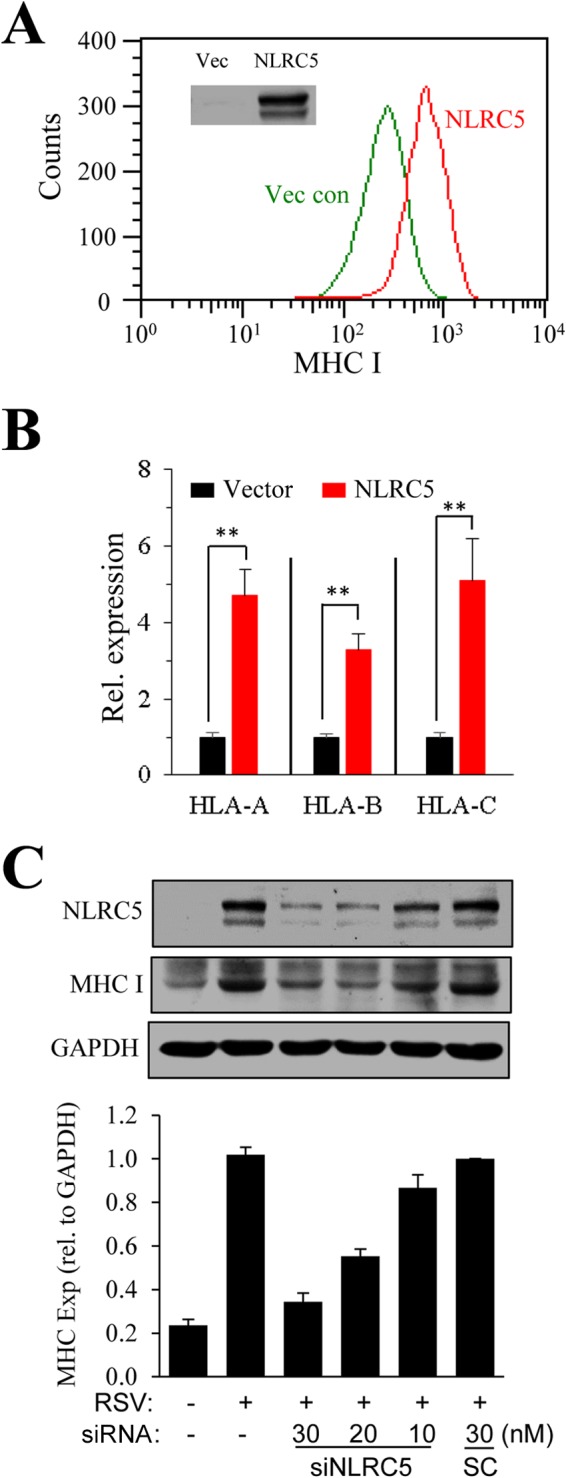
Correlation of NLRC5 expression and MHC-I induction. (A) Overexpression of NLRC5 enhances MHC-I expression. A549 cells were transiently transfected with an empty vector (Vec con) or with p3x-FLAG-NLRC5 for 36 h. Surface expression of MHC-I was determined by FACS. The inset shows NLRC5 expression determined by Western blotting. The experiment was performed twice independently. (B) In parallel experiments, gene expression of MHC-I molecules in the samples was determined by qPCR. The results are representative of three independent experiments. The data are presented as means and SD of duplicate samples. **, P ≤ 0.01. (C) Suppression of NLRC5 expression by siRNA inhibits MHC-I induction. A549 cells were treated by transfection with an SC or with siNLRC5 number 1 at various concentrations (10, 20, and 30 nM) for 24 h. The cells were left uninfected or infected with RSV for another 36 h. NLRC5 and MHC-I expression (Exp) was determined by immunoblotting. The experiment was performed three times independently. The fold change in the ratio of MHC-I to GAPDH was measured in the three blots using ImageJ software and plotted by normalizing to the ratio in the SC, set as 1.
