FIG 4.
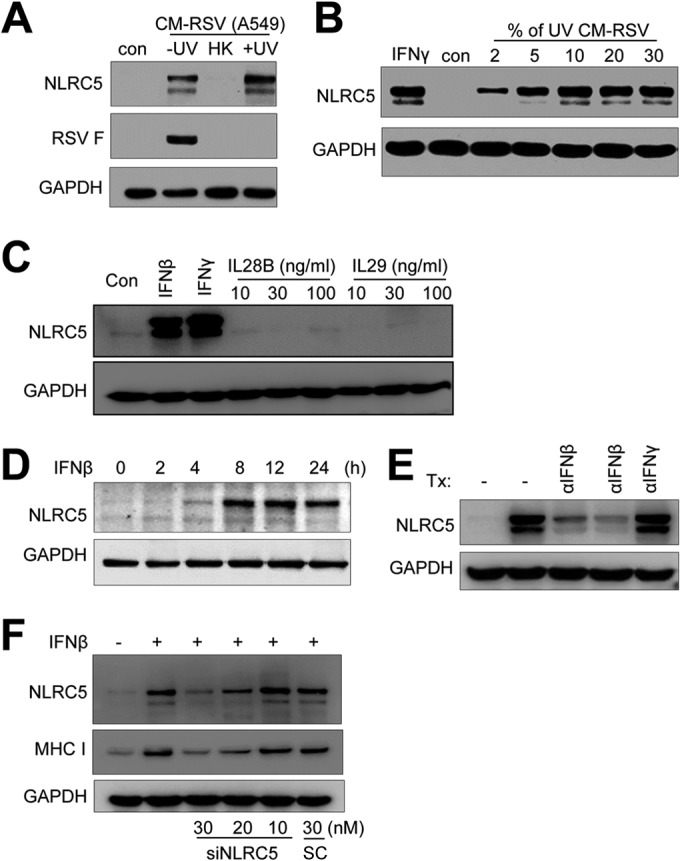
RSV promotes NLRC5 expression in A549 cells through IFN-β secretion. (A and B) Conditioned medium contains NLRC5-inducing activity. (A) A conditioned medium from RSV-infected A549 cells (CM-RSV A549) was UV irradiated to deactivate RSV (+UV), heat inactivated (HK), or left untreated (−UV). The medium was then mixed with fresh DMEM at a 10% ratio and used to treat A549 cells. (B) Dose response of NLRC5 induction to the conditioned medium. UV-irradiated conditioned medium was mixed with fresh DMEM at various ratios (percent [vol/vol]) and used to treat A549 cells. NLRC5 induction was determined by Western blotting. The expression of viral F protein was determined to show the effect of UV irradiation or heat deactivation on infectious virions. The experiment was performed two times independently. (C) Induction of NLRC5 by recombinant interferons. A549 cells were treated with IFN-β (100 U/ml), IFN-γ (100 U/ml), and IL-28B or IL-29 (10, 30, and 100 ng/ml) for 24 h. Cells were harvested, and NLRC5 induction was detected by Western blotting. GAPDH expression was used as an internal control. (D) Time course of NLRC5 induction by recombinant IFN-β. A549 cells were treated with recombinant IFN-β at 100 U for the indicated times. NLRC5 induction was determined by immunoblotting. GAPDH was the loading control. (E) Immunodepletion of IFN-β removes NLRC5-inducing activity. Aliquots (100 μl) of UV-irradiated conditioned medium were left untreated or incubated at 4°C with anti-IFN-β (10 μg/ml and 30 μg/ml) or anti-IFN-γ (30 μg/ml) for 60 min. The immunocomplexes were removed by protein A-Sepharose beads. The supernatants were mixed with fresh DMEM at 5% (vol/vol) and tested on A549 cells for NLRC5-inducing activity. The results are representative of two independent experiments. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Tx, treatment. (F) Suppression of NLRC5 expression inhibits NLRC5 and MHC-I induction by IFN-β. A549 cells were transfected with scrambled control or with siNLRC5 number 1 (10, 20, or 30 nM) for 24 h. The cells were then treated with 100 U of IFN-β for 24 h. NLRC5 and MHC-I expression was determined by Western blotting. GAPDH expression was the loading control.
