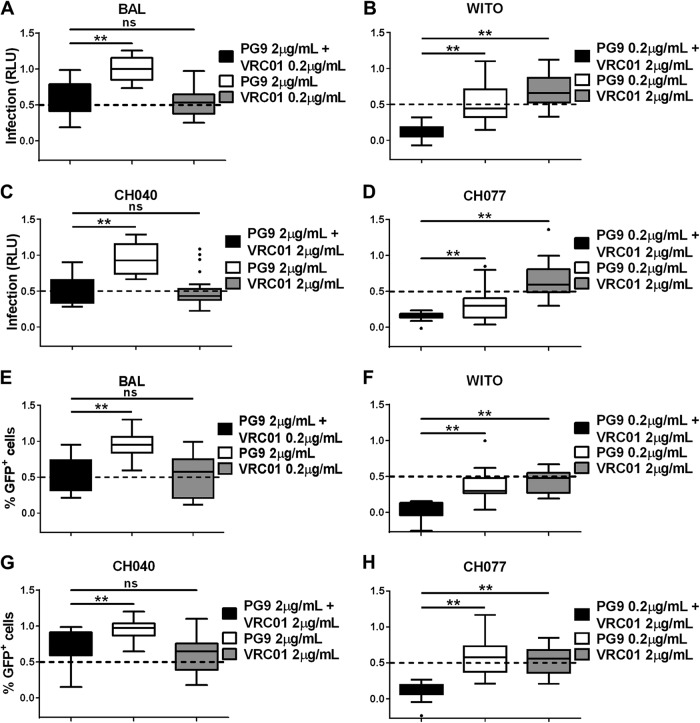
FIG 4.
Neutralization of cell-associated virus by combination of two gp120-specific broadly neutralizing antibodies. Two HIV-1-directed antibodies, PG9 and VRC01, were combined at concentrations that have a partial effect to no effect on cell-associated virus infection when used individually. Infection was evaluated in TZM-bl (A to D) or A3R5 (E to H) target cells with cell-associated HIV-1 BAL (A and E), WITO (B and F), CH040 (C and G), and CH077 (D and H). Infection was measured by quantifying the RLU of TZM-bl cells (A to D) or the percentage of GFP+ (Far Red−) A3R5 cells (E to H) for each cell-associated Env variant in the presence of the indicated concentrations of antibodies, used in combination or alone, where 1 is equal to 100% infection. Results were normalized and expressed as box-and-whisker plots illustrating the median, first and third quartiles, and range with outliers (solid circles). Significant differences were assessed with exact Wilcoxon rank sum tests and Holm's adjustment to compare each combination of antibodies to the single-antibody treatment. A significant difference is represented by ** (P < 0.005), and a nonsignificant difference is represented by “ns.”