FIG 5.
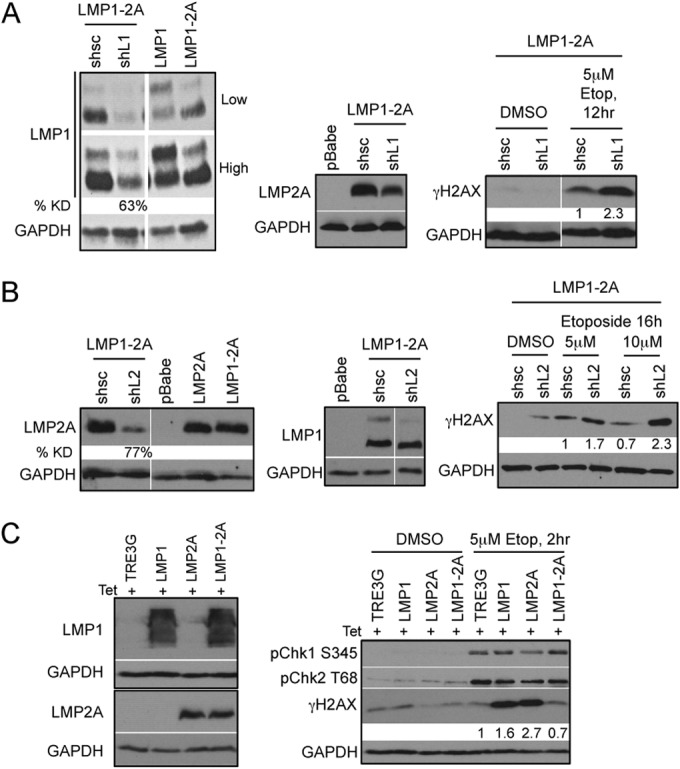
Reduction of γH2AX phosphorylation is dependent on the coexpression of LMP1 and LMP2A. Immunoblot analysis of efficient LMP1 (A) and LMP2A (B) knockdown (KD) 5 days after transduction with control (shsc) and specific (shL1 and shL2) shRNA constructs. LMP1 and LMP2A expression was normalized to that of the GAPDH loading control by densitometry with Image J software and represented as percent knockdown (% KD) compared to that of shsc control cells. HK1 LMP1-2A cells with LMP1 and LMP2A KD treated with 5 μM etoposide (Etop) were analyzed for DDR signaling proteins by immunoblotting. Changes in γH2AX levels were normalized to that of GAPDH by densitometry with Image J software and represented as fold change relative to the level for shsc control cells. (C) Transient expression of LMP1 and LMP2A in HEK293 cells was induced by 200 ng/ml doxycycline treatment for 48 h and analyzed by immunoblotting with LMP1-specific S12 antibody and LMP2A-specific 14B7 antibody. Lysates were analyzed 2 h after treatment with 5 μM etoposide for DNA damage signaling proteins and γH2AX phosphorylation. Changes in γH2AX phosphorylation levels were normalized to that of GAPDH by densitometry with Image J software and represented as fold change relative to the level for TRE3G control cells.
