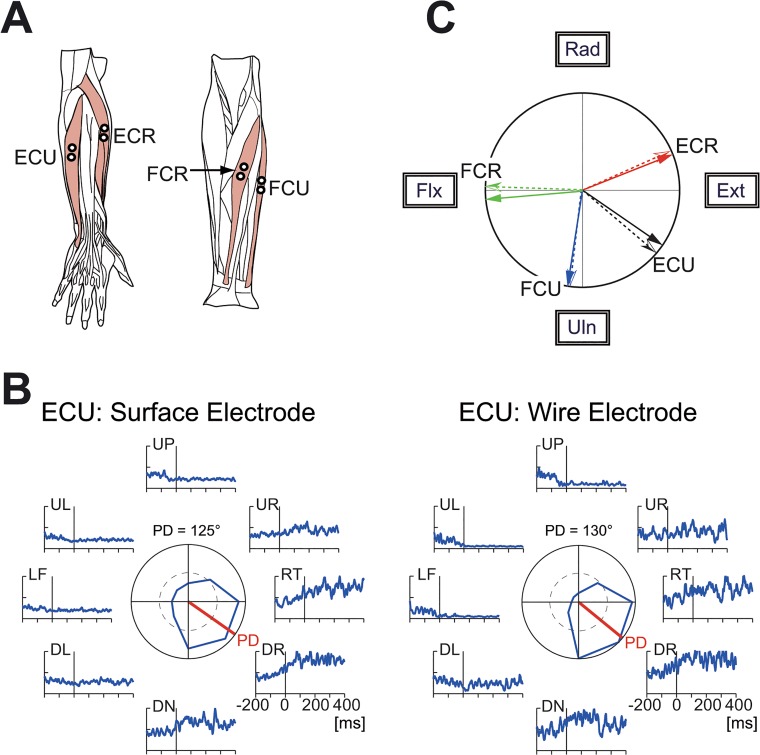
Fig 2. Muscles related to the wrist joint and comparison of surface and wire electromyography (EMG) signals.
(A) The four wrist prime movers from which EMG activity was recorded. ECR, extensor carpi radialis; ECU, extensor carpi ulnaris; FCU, flexor carpi ulnaris; FCR, flexor carpi radialis. We recorded the activity of the extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL) and extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) together as ECR because these two muscles are indistinguishable with surface electrodes. (B) Comparison of the surface and wire EMG activity recorded simultaneously from ECU. The raw EMG signals were filtered (τ = 10 ms) [18], fully rectified, and averaged for 10 trials. The polar plot in the center shows muscle activity within an interval of ±25 ms relative to the movement onset. The red bars in the center indicate the preferred direction, which was calculated with cosine fitting [18]. (C) Correspondence of the preferred direction of EMG activity recorded simultaneously with surface electrodes (solid arrows) and wire electrodes (dotted arrows). ECR surface = 68°, wire = 66°; ECU surface = 125°, wire = 130°; FCU surface = 189°, wire = 187°; FCR surface = 265°, wire = 272°.