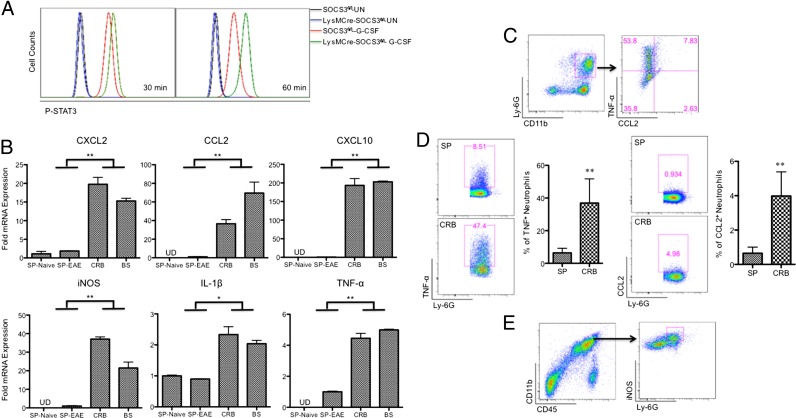
FIGURE 5.
Neutrophils are pathogenic in the development of atypical EAE by producing proinflammatory chemokines and cytokines. (A) Cells from the bone marrow of SOCS3fl/fl or LysMCre-SOCS3fl/fl mice were treated with G-CSF (10 ng/ml) for 30 and 60 min, and then cells were stained with Abs to CD11b, Ly-6G, and p-STAT3. (B) CD45+CD11b+Ly-6ClowLy-6G+ neutrophils were sorted from splenocytes of naive LysMCre-SOCS3fl/fl mice or from splenocytes and CRB- and BS-infiltrating mononuclear cells at the peak of disease from LysMCre-SOCS3fl/fl mice with atypical EAE (n = 4 mice). mRNA was isolated and analyzed for CXCL2, CCL2, CXCL10, iNOS, IL-1β, and TNF-α. Mean ± SD. Data represent fold induction compared with neutrophils isolated from naive LysMCre-SOCS3fl/fl splenocytes. Fold induction of indicated genes was compared between CRB- and BS-infiltrating neutrophils and neutrophils from SP of naive mice or EAE mice. Data represent three individual experiments. (C) CRB-infiltrating mononuclear cells isolated from LysMCre-SOCS3fl/fl mice at the peak of atypical EAE were stimulated in the presence of LPS (10 ng/ml) with GolgiStop for 4 h and stained for the surface markers CD45, CD11b, Ly-6C, and Ly-6G (left panel), and by intracellular flow for TNF-α and CCL2 (right panel) (n = 4 mice). (D) CRB-infiltrating mononuclear cells and splenocytes isolated from LysMCre-SOCS3fl/fl mice at the peak of atypical EAE were stimulated in the presence of LPS (10 ng/ml) with GolgiStop for 4 h and stained for the surface markers CD45, CD11b, Ly-6C, and Ly-6G (left panel), and by intracellular flow for TNF-α (left panel) or CCL2 (right panel) (n = 4 mice). (E) CRB-infiltrating mononuclear cells isolated from LysMCre-SOCS3fl/fl mice at the peak of atypical EAE were stained with Abs to CD45, CD11b, Ly-6G, and iNOS. Cells were first gated on CD11b and CD45 (left panel), and then gated on Ly-6G and iNOS (right panel). Representative flow cytometry plot of iNOS+ neutrophils (n = 4 mice). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.