Fig 6.
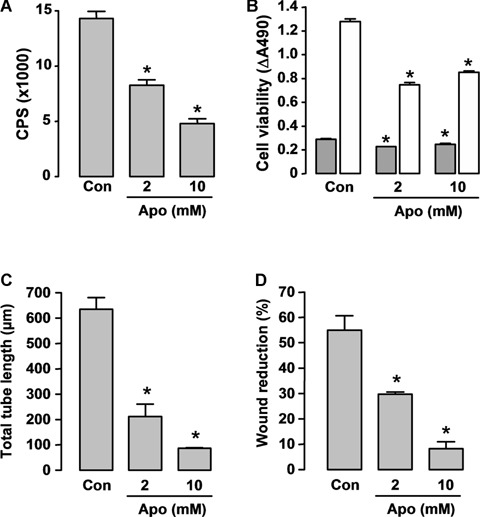
Effects of the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase inhibitor apocynin on (A) NADPH oxidase activity, (B) cell viability and (C, D) angiogenic responses in cultured Human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC) cells. (A) Cells were detached by trypsinization and resuspended in Hank's balanced salt solution. Apocynin (Apo) was added 60 min before assay. Superoxide release was measured by lucigenin (5 μM)-enhanced chemiluminescence after stimulation with 100 μM NADPH in a topcount microplate reader (model 9912, Packard). The results are expressed as count per second (CPS) per 105 cells (n = 5). (C) Con, DMSO control. (B) Cell survival was assessed 24 (grey bars) and 72 hrs (hatched bars) after apocynin treatment with the CellTiter-96 AQueous One Solution kit, and the results are expressed as differences of absorbance at 490 nm between wells containing cells and buffer only (background) (n = 4). (C) In vitro angiogenesis was assessed by the tube formation assay (observed 6 hrs after cell plating on Matrigel, n = 3). Apocynin was added at the time of plating. (D) Wound-healing assay in HMECs observed 18 hrs after scratching (n = 3). Apocynin was added at the time of scratching. * P < 0.05 versus corresponding control (Con), one-way anova.
