Fig 2.
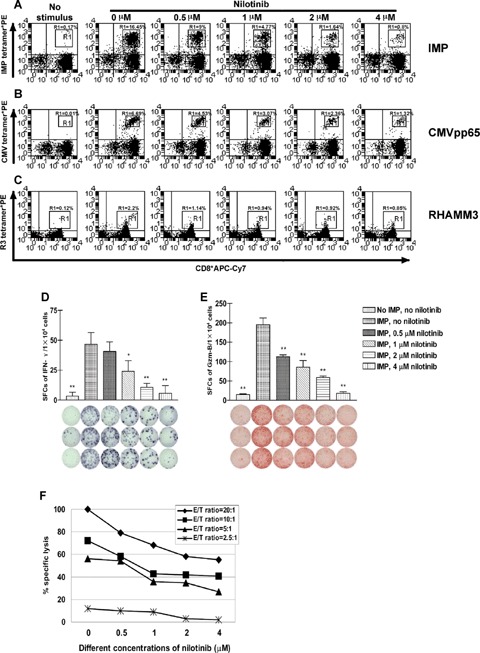
Nilotinib inhibits IMP-, CMV- and RHAMM-specific CD8+ T lymphocytes as a function of the concentration of and the incubation time with the drug. CD8+ T lymphocytes from patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) were subjected to one round of stimulation with irradiated autolo-gous CD8v− APCs pulsed with influenza matrix protein (IMP), cytomegalovirus (CMV) or RHAMM derived R3 peptide in the absence or presence of 0.5 μM, 1 μM, 2 μM and 4 μM nilotinib as described in ‘Material and methods’. The dot plots show the percentage of HLA-A2/IMP- or HLA-A2/CMV-or HLA-A2/R3- tetramer*PE positive CD8+ T lymphocytes. Effects of nilotinib on the expansion of IMP-specific CD8+ T lymphocytes over 8 days of mixed lymphocyte peptide cultures (MLPC) are displayed in Panel A, effects on the expansion of CMV-specific CD8+ T lymphocytes in Panel B, and effects on the expansion of RHAMM derived R3-specific CD8+T lymphocytes in Panel C. The proliferation of IMP-, CMV- or R3-specific CD8+ T lymphocytes was inhibited in a dose-dependent manner. The figure displays representative results from one of four consecutive experiments with similar results. The T cell reaction was inhibited in a dose-dependent fashion as analysed by ELISPOT assays for spot-forming cells (SFCs) of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) (Panel D) and granzyme B (Gzm-B) (Panel E) after 8 days of MLPC in the absence or presence of different concentrations of nilotinib. As evaluated by 51Cr release assay (Panel F), the lysis of IMP-pulsed T2 cells by cognate peptide specific CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes generated during one round of MLPC was affected by nilotinib in a dose-dependent manner at different E/T ratios. The figures show results from one representative experiment. All assays were performed in triplicate. Error bars indicate the SD. Significant differences from the non-nilotinib-treated group are indicated, *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
