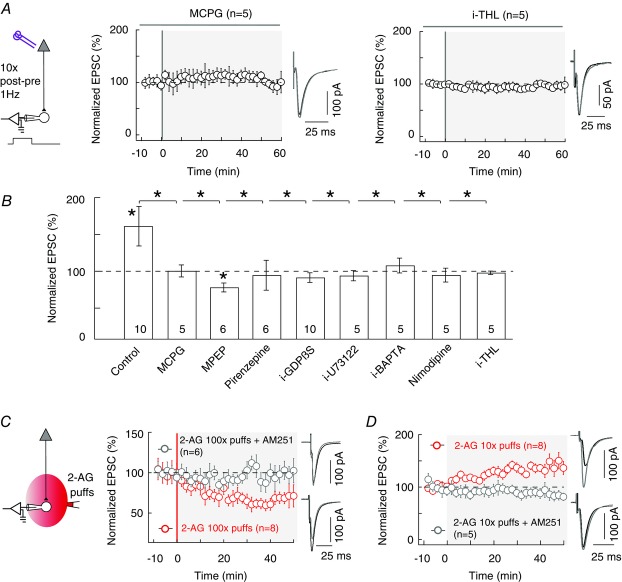
Figure 3. Induction of tLTP by 10 pairings involves postsynaptic 2-AG signalling.
A and B, summary graphs of pharmacological experiments delineating the intracellular signalling pathways involved in 10 pairings-induced tLTP. A, tLTP was prevented by inhibition of group-I mGluR with MCPG (500 μm, n = 5) or of DAGLα by i-THL (10 μm, n = 5; the prefix ‘i’ indicates that the drug was applied in the recorded postsynaptic neuron through the patch-clamp pipette). B, summary bar graphs showing that LTP was mediated by mGluR5 and M1R. Indeed, tLTP was prevented by inhibition of group-I mGluR with MCPG (500 μm, n = 5) and more specifically by inhibition of mGluR5 with MPEP (10 μm, n = 6); inhibition of M1R also prevented tLTP (1 μm pirenzepine, n = 6). Downstream of these receptors, inhibition of postsynaptic G-protein-coupled receptors (with 2 mm i-GDP-β-S, n = 10), PLCβ (with 5 mm i-U73122, n = 5), DAGLα (with 10 μm i-THL, n = 5) shows the involvement of PLCβ and 2-AG synthesis. In addition, bar graphs show the involvement of postsynaptic intracellular calcium (inhibited by 10 mm i-BAPTA, n = 5) and VSCCs (inhibited by 1 μm nimodipine, n = 5), since their blockade prevented the expression of tLTP. C, repeated brief application of 2-AG induces LTD. A serie of 100 2-AG puffs (100 μm, 300 ms duration each) delivered at 1 Hz at the vicinity (50–100μm) of the recorded striatal neuron, induced LTD in the absence of any STDP protocol (n = 8). This 2-AG-mediated LTD was prevented by AM251 (3 μm, n = 6). D, limited brief application of 2-AG induces LTP. Application of 10 2-AG puffs (100 μm, 300 ms duration each) delivered at 1 Hz was able to induce LTP in the absence of any STDP paired stimulation (n = 8). Inhibition of CB1R with bath-applied AM251 (3 μm, n = 5) prevented the induction of LTP by 2-AG puffs. Representative traces are the average of 15 EPSCs during baseline recording (black traces) and 50 min after STDP protocol (grey traces). Error bars represent SD. *P < 0.05.