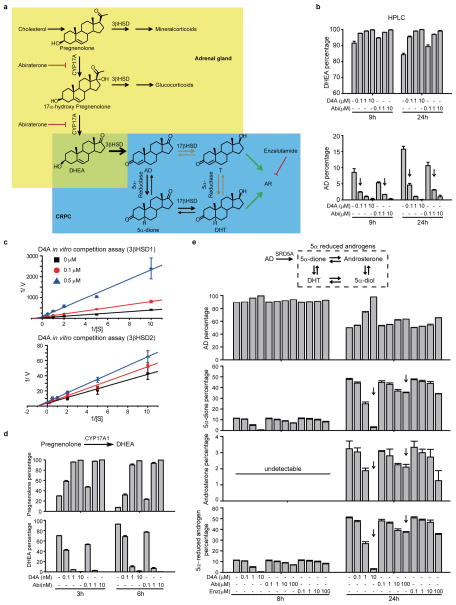
Figure 2.
D4A inhibits 3βHSD, CYP17A, and 5α-reductase enzymatic activity in the androgen pathway. a, Schematic of the steroidogenesis pathway from adrenal precursors to DHT and AR stimulation in CRPC. b, D4A inhibits 3βHSD1 activity in LNCaP. Cells were treated with [3H]-DHEA with 0.1, 1 or 10 μM D4A and Abi, for 9 and 24 hours. DHEA and AD were quantified by HPLC. Arrows denote AD percentage for 0.1 μM D4A and 1 μM Abi treatment groups. c, Lineweaver-Burk plots of pregnenolone metabolism and D4A inhibition of human 3βHSD1 and 3βHSD2 activity. D4A shows mixed competitive-noncompetitive inhibition for 3βHSD1 and noncompetitive inhibition for 3βHSD2. d, CYP17A1 inhibition with D4A is comparable to Abi. 293 cells stably expressing CYP17A1 were treated with 0.1, 1 or 10 nM D4A, or Abi, together with [3H]-pregnenolone for 3 and 6 hours. Pregnenolone and DHEA were separated and quantified by HPLC. e, D4A but not Abi or enzalutamide inhibits 5α-reductase activity. LAPC4 cells were treated with [3H]-AD and the indicated drug concentrations. Steroids were quantified by HPLC. Arrows denote 5α-reduced androgen percentage for 10 μM D4A and 100 μM Abi treatment groups. All experiments performed with biological replicates (n = 3) and repeated independently three times. All results are shown as mean ± s.d..