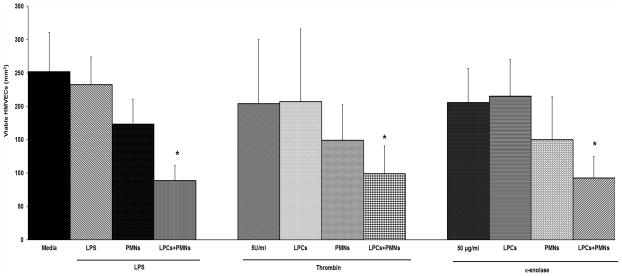
Figure 2. Thrombin and α-enolase serve as the first event in a two-event model of PMN-mediated HMVEC cytotoxicity.
The number of viable HMVECs/mm2 is shown as a function of treatment group. Media treated controls are the solid bar in the left group. Treatment alone with endotoxin (LPS [2μg/ml]), thrombin, α-enolase, lysophosphatidylcholines (LPCs, a PMN priming agent), or PMNs did not cause significant HMVEC toxicity. In addition HMVECs activated with LPS, thrombin, or α-enolase and co-cultured with PMNs did not demonstrate a significant decrease in viable HMVECs. However, HMVECs activated with LPS, thrombin, or α-enolase, co-cultured with PMNs and then incubated with LPCs demonstrated significant decrease in viable HMVECs (last bar on the right in each group) (*=p<0.05 vs. media-treated HMVECs, n=5).