Fig. 2.
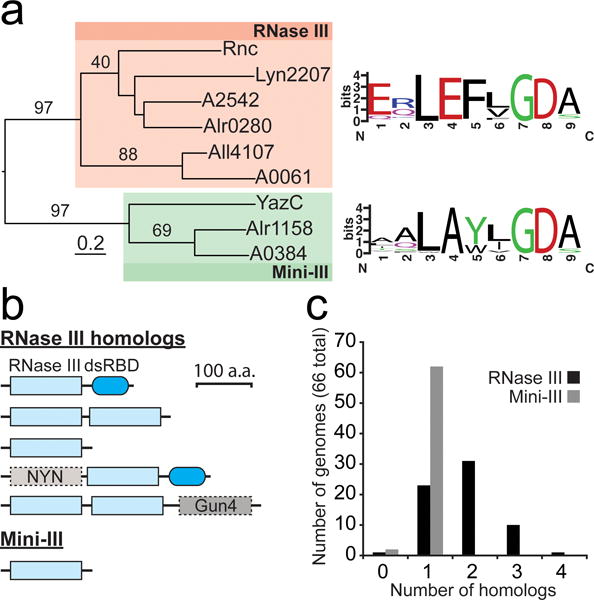
Diversity and distribution of RNase III homologs in cyanobacteria
(a) Phylogenic relationship between RNase III and Mini-III homologs in Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 (Alr0280, Alr4107, and Alr1158), Leptolyngbya sp. PCC 6406 (Lyn2207), PCC 7002 (A2542, A0061, and A0384), E. coli (Rnc), and B. subtilis (YazC). The RNase III homologs all contained the typical domain structure with a single, N-terminal RNase III domain and a C-terminal dsRBD, with the exception of Lyn2207, containing only a single RNase III domain. Conservation logos (weblogo.berkeley.edu) corresponding to the RNase III signature motif generated from multiple sequence alignments of RNase III and Mini-III homologs in 65 and 64 cyanobacterial genomes, respectively. (b) Domain architecture of RNase III and Mini-III homologs in cyanobacteria. (c) Number of RNase III and Mini-III homologs in 66 diverse cyanobacterial genomes. Additional details can be found in “Materials and Methods”. RNase III homologs in each analyzed genome are listed in Online Resource 4.
