Fig. 3.
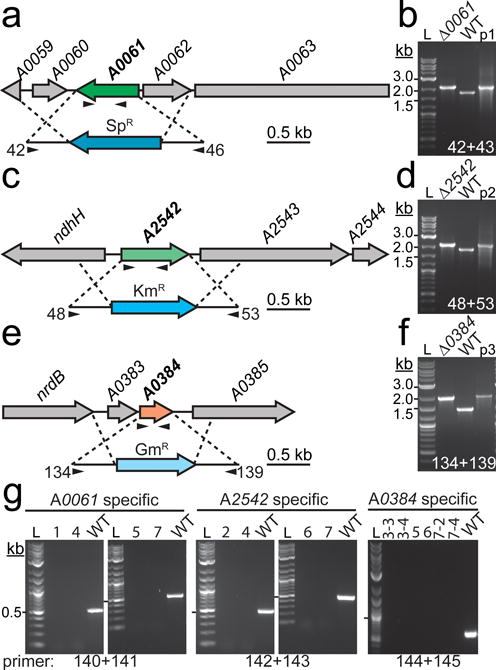
Genetic deletion and segregation analysis of RNase III homologs in PCC 7002
Targeted gene replacement via homologous recombination was used to replace the open reading frames of (a) A0061, (c) A2542, and (e) A0384 with three different antibiotic resistance cassettes. Insertion of the antibiotic resistance cassette into the correct genetic locus was confirmed by PCR using primers flanking the WT loci (b, d, and f). Arrows in (a), (c), and (d) below the gene and insertion cassette indicate approximate location of gene specific and flanking primers, respectively. The plasmid (p1, pJCC249; p2, pJCC250; p3, pJCC251) used to transform the mutant was used as a positive size control and WT genomic DNA was used as a negative size control. WT sized bands were not observed in the mutant strains, indicating that the regions of interest are homozygous for the mutation. (g) Gene specific primers were used to confirm segregation of the insert by PCR. In this case, WT genomic DNA served as the positive control. Lanes: 1, Δ0061; 2, Δ2542; 3, Δ0384; 4, Δ0061/2542; 5, Δ0061/0384; 6, Δ2542/0384; 7, Δ0061/2542/0384. The 0.5 kb size band is indicated with a hash mark next to the 2-log DNA ladder (L). Oligonucleotides used in cloning and segregation analysis are listed in Online Resource 2. Refer to “Materials and Methods” for additional details about strain construction and segregation analysis.
