Fig. 7.
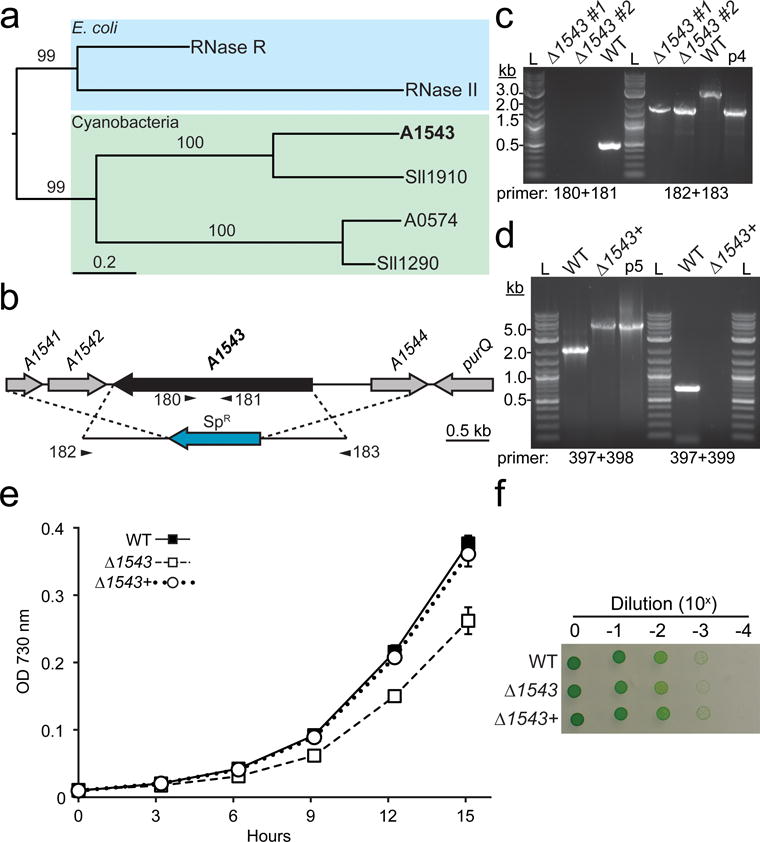
Generation and physiological characterization of a Δ1543 mutant in PCC 7002
(a) Phylogenetic relationship between RNase II/R homologs in E. coli (RNase R and RNase II), PCC 7002 (A1543 and A0574), and Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 (Sll1910 and Sll1290). Scale bar indicates the number of substitutions and values above branches indicate support from 100 bootstrap replicates. (b) The open reading from of A1543 was replaced with a SpR cassette via targeted homologous recombination. Gene specific and flanking primers used in segregation analysis are shown below the gene and the integration cassette, respectively. (c) Segregation of the mutation was confirmed using gene specific and flanking primers. Two independent Δ1543 clones were analyzed (#1, and #2). WT genomic DNA was used as a control. The plasmid used to generate the Δ1543 mutant (p4, pJCC254) was used as a positive size control. L, 2-log ladder. (d) To genetically complement the Δ1543 mutant strain, the native A1543 gene, including the ~700 bp upstream and ~80 bp downstream intergenic regions, was targeted to the glpK neutral site in the Δ1543 background. Segregation of the glpK locus in the resulting strain (Δ1543+) was confirmed using flanking and gene specific primers. Growth of the WT, Δ1543, and Δ1543+ strains in liquid bubbling culture (200 μmol photons m−2 s−1) (e) and solid medium (120 μmol photons m−2 s−1) in ambient CO2 (f). Error bars represent s.d. for three biological replicates. Growth on solid medium was performed in quadruplicate; a representative image is shown.
