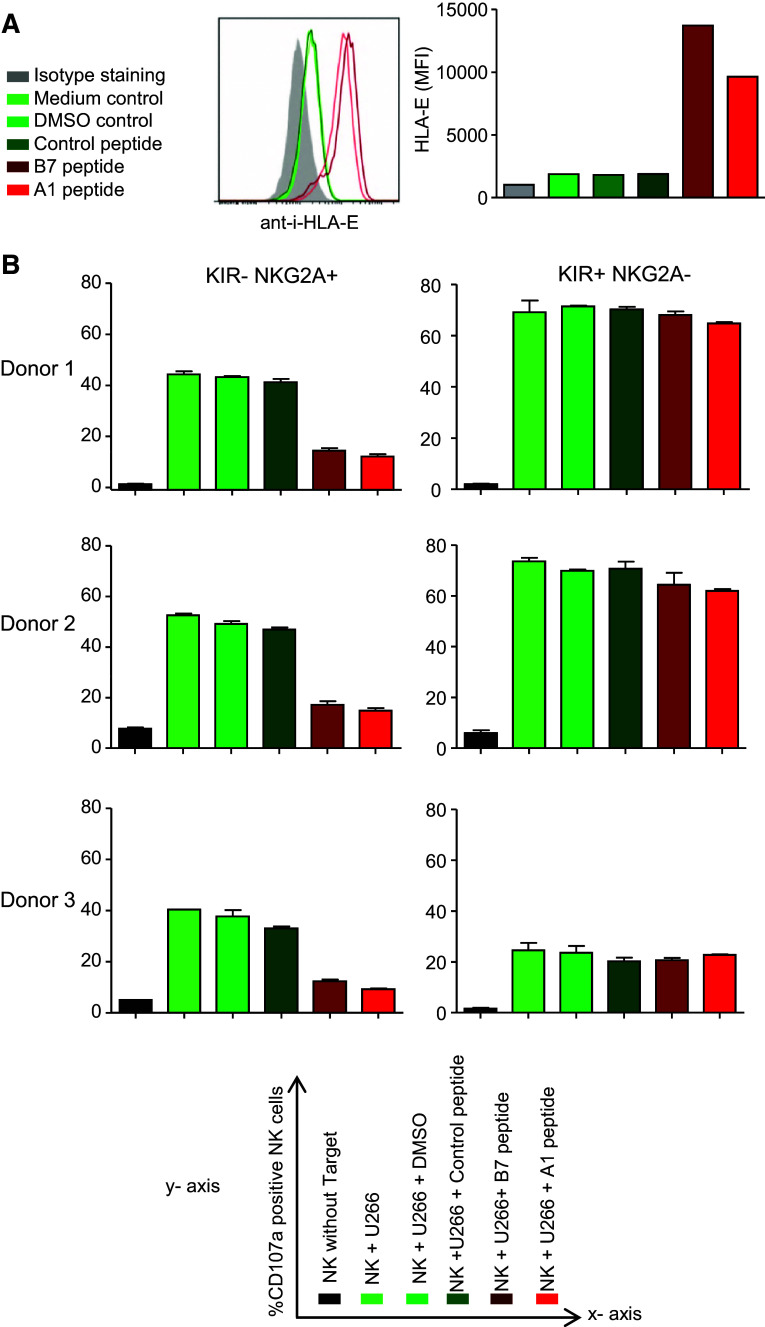
Fig. 6.
Upregulation of HLA-E renders NK-sensitive myeloma cells resistant to IL-2-activated NKG2A+ NK cells. a U266 cells were incubated for 12 h at 37 °C with 500 µM A1- or B7- HLA-E binding peptides. As control, U266 cells were incubated with a control (non-binding) peptide, DMSO or medium. HLA-E surface expression was determined by flow cytometry after staining of the cells with anti-HLA-E or an IgG1 isotype control. Shown is a representative histogram with, in gray, the isotype control staining, in green, the control incubations and, in red, the conditions with HLA-E binding peptides. Graph shows MFI values from the histogram. b Myeloma cells were pre-incubated with peptides and controls as described in A for 2 h. Then, IL-2-activated NK cells were added and the cells were co-cultured for an additional 12 h. Percentage of CD107a+ cells was determined for three donors in NKG2A+ KIR− and in NKG2A−KIR+ NK cell subsets. Graphs depict means of duplicate cultures per donor. X axis legend is given in the lower panel of the figure