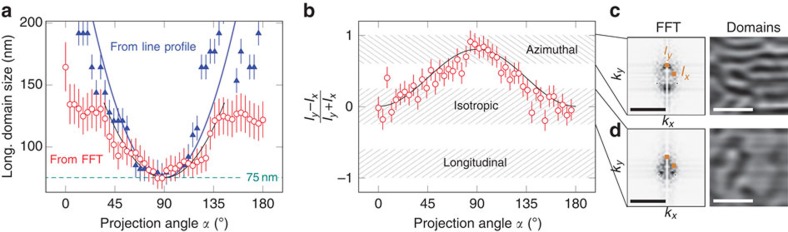
Figure 6. Angle dependence of the magnetic domain pattern.
(a) Domain width in longitudinal direction reveals smallest values at α≈90°. Data are extracted from line profiles of real-space images (solid triangles) and from peak positions of FFT images (open circles), respectively. The uncertainties are determined by s.d. and the resolution in the reciprocal space. (b) Continuous transition from an isotropic/random domain configuration into an azimuthal ordering obtained from FFT. Ix,y is defined in c. Solid lines serve as a guide to the eye. Reciprocal (FFT) and real-space (domain) images of azimuthal (c) and isotropic (d) domain patterns. Dark and bright contrast refer to a magnetization pointing outside and inside the tube, respectively. Scale bars are 10 nm−1 and 500 nm, respectively