Figure 1.
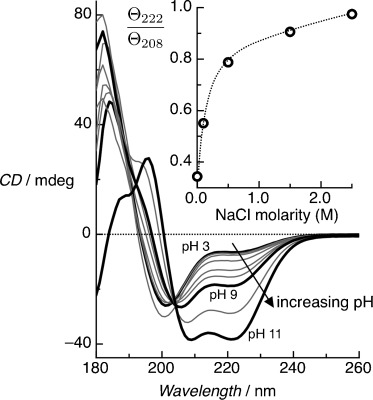
Solution-phase CD spectra for the BASE-C peptides as a function of pH. Pronounced CD minima at 222 nm and 208 nm, characteristic of the formation of α-helical secondary structures, are observed only above pH 9. At pH 11, the ratio Θ222/Θ208 approaches 1, indicating that the helical peptides assemble predominantly into stable coiled-coil homodimers. Measurements were performed in 10 mm sodium phosphate and at a peptide concentration of 65 μm. Inset shows Θ222/Θ208 versus ionic concentration, demonstrating that helical peptides form at pH 3 with NaCl concentrations ≥0.5 m, with stable coiled-coil homodimer assembly dominating at 2.5 m NaCl. Measurements were performed in 10 mm sodium phosphate at pH 3.
