Fig. 1.
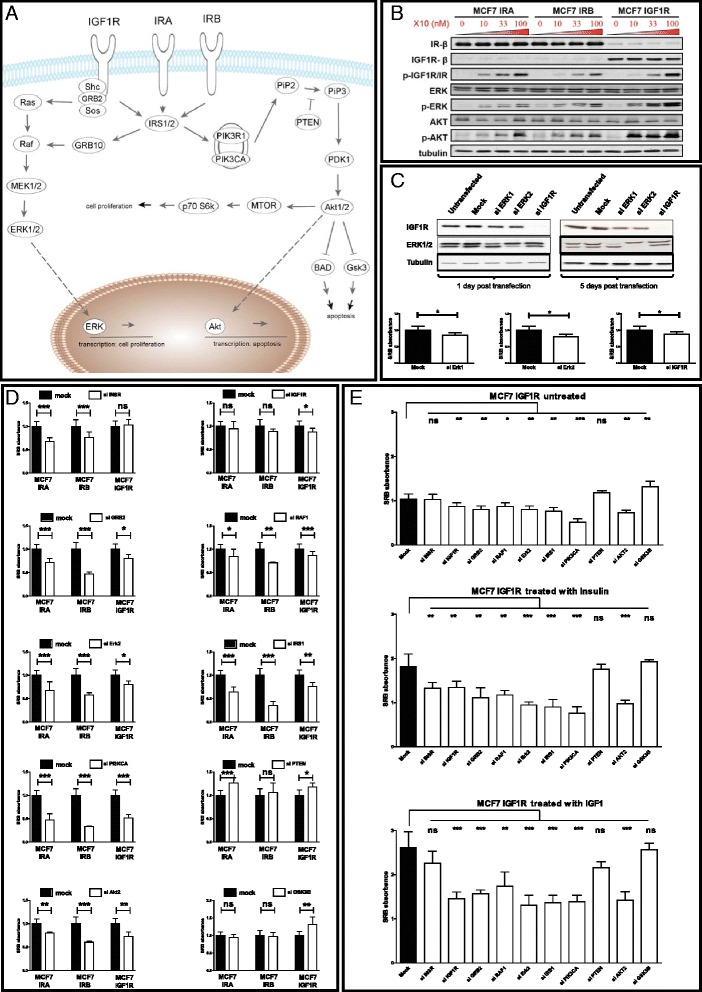
Knockdown of signaling components critical in the INSR and IGF1R pathway reveals common canonical core in IRA-, IRB- and IGF1R-induced proliferation signaling. a The canonical INSR and IGF1R signaling pathway with the focus on proliferative and apoptotic biological outcomes. b Western blot analysis of the cell line panel, based on the human breast cancer cell line MCF7 with stable retroviral overexpression (IRA, IRB and IGF1R) in combination with a stable short hairpin knockdown (INSR and IGF1R). Cells have been treated with 0, 10, 33 or 100 nM of insulin X10 for 30 min. Downstream signaling pathway activation of the receptors is intact as is indicated by the dose-dependent activation of p-ERK/p-AKT. c Western blot analysis of siRNA transfection efficiency in the MCF7 IGF1R cell line, 1 day and 5 days posttransfection and the effect of the knockdown on proliferation measured with the SRB proliferation assay. d The effect of transient knockdown of ten important signaling molecules (INSR, IGF1R, GRB2, RAF1, ERK2, IRS1, PIK3CA, PTEN, AKT2 and GSK3B) in the INSR and IGF1R signaling pathways on SRB proliferation measured in the different MCF7 derivatives (MCF7 IRA, MCF7 IRB and MCF7 IGF1R). e The effect of treatment and knockdown of key signaling molecules in INSR and IGF1R signaling on SRB proliferation measured in MCF7 IGF1R. (* p <0.05, ** p <0.01, *** p <0.001). IGF1R insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor, INSR insulin receptor, IRA A isoform of INSR, IRB B isoform of INSR; siRNA small interfering RNA, SRB sulphorhodamine B
