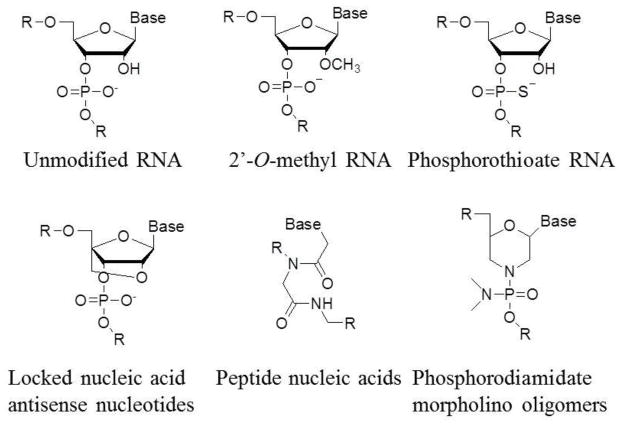
Figure 3.
Chemical modifications of AMOs. 2′-O-methyl RNA is modified by changing the 2′ hydroxy group of the ribose into methoxy group; phosphorothioate RNA introduces the sulfur substitution of a non-bridging oxygen to make a phosphorothioate linkage between nucleotides; locked nucleic acid links 2′, 4′ of the ribose by methylene bridge to form a bicyclic nucleotide; peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) substitute a peptide bond at the 1′ amide linkage to the base. Phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers (PMOs) contain morpholine rings instead of deoxyribose rings that are linked through phosphorodiamidate groups instead of phosphates.