Figure 2.
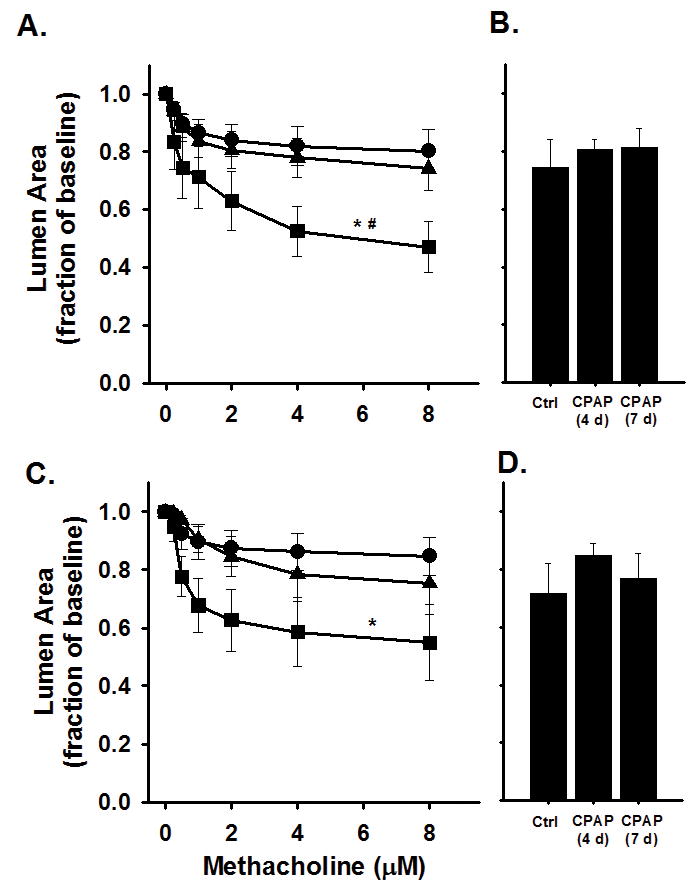
Airway responses to methacholine challenge in the in vitro living lung slice preparation from 21 day old (A–B) male and (C–D) female mice that received either 4 (triangles) or 7 (squares) days of neonatal CPAP (6cmH2O). Note, 7 days of CPAP increased AW reactivity in small AWs of both male (A) and female (C) mice compared to control (Ctrl, circles) animals. The large AWs of both male (B) and female (D) mice were not affected by CPAP. “Small” AWs (A and C) are defined as baseline lumen area <7000 pixels; “large” AWs (B and D) are defined as baseline lumen area >7000 at baseline. *indicates significant difference in the slope of the response to methacholine of Ctrl animals (N=6–8 airways from 4–5 mice/group); #indicates significant difference in the slope of the response to 4days of CPAP (p<0.05).
