Figure 3.
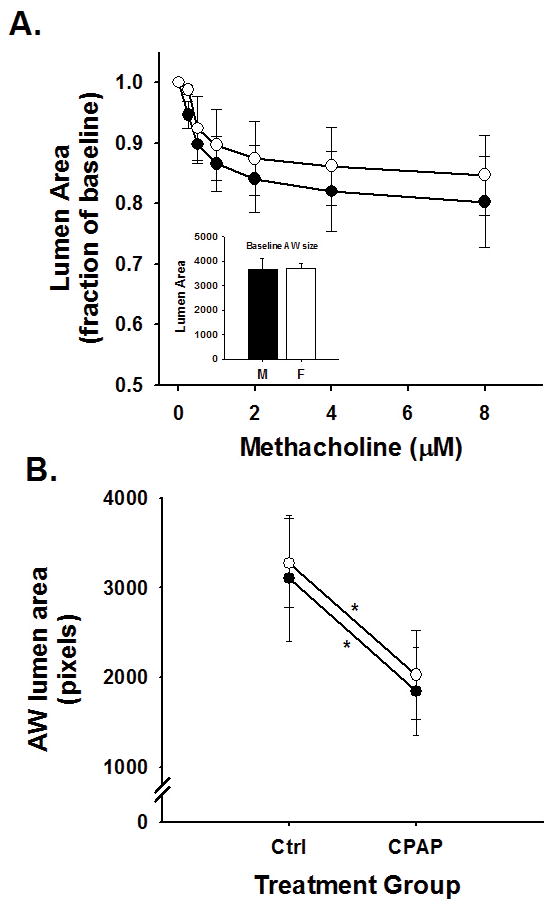
Small AW (<7000 pixel baseline lumen area) responses to methacholine challenge in (A) 21 day old male (black symbols) and female (open symbols) control mice and (B) the effects of 7 days of neonatal CPAP on small AW responses to maximum (8μM) dose of methacholine. AW reactivity to methacholine was similar between male and female control mice (A) and both sexes were equally affected by 7 days of neonatal CPAP (B). Values in A are expressed as a fraction of baseline lumen area; whereas values in B are expressed as absolute AW area at maximum contraction (8μM, methacholine). Inset: average values for the mean AW size (at baseline) for both male and female mice was not different. *indicates significant slope of the response to methacholine (p<0.05); however, there was no difference in the slopes between sexes, suggesting males and females are equally sensitive to CPAP treatment.
