Figure 5.
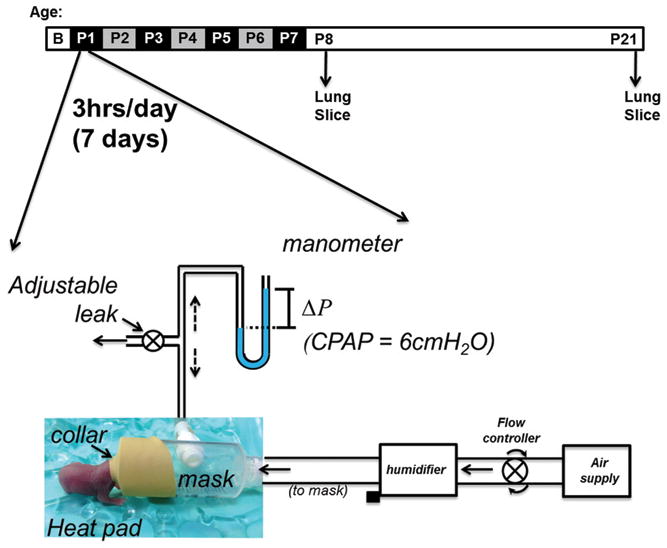
Schematic of the setup used to administer CPAP non-invasively to neonatal mice. A collar is fitted over the face through which air flows to a downstream manometer. An adjustable leak allows optimization of the back-pressure (i.e. CPAP) to be applied to the mask and AWs of the mouse. The level of CPAP can be accurately measured using the manometer (ΔP, pressure difference) and adjusted accordingly. The protocol for CPAP delivery (indicated above) consisted of 6cmH2O, 3 hours/day, for 7 consecutive days from postnatal age 1–7 days (P1-P7). Airway responses to methacholine challenge were assessed in the in vitro living lung slice preparation the day after (P8) and ~2 weeks after CPAP treatment ended. Note, however, CPAP was administered for only 2 hours on the first day (P1) instead of 3hrs to minimize the duration the litter was separated from the dam.
