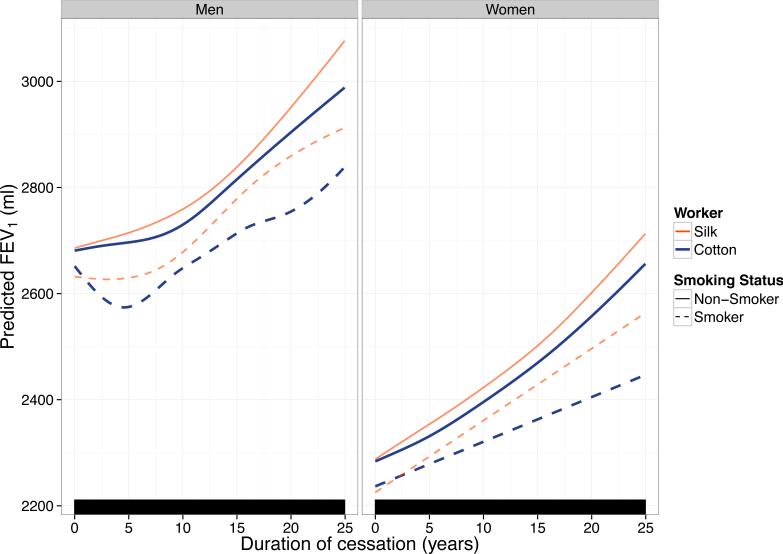
Figure 1. Adjusted effect of work cessation on FEV1, stratified by gender, occupational exposure, and smoking status based on a generalized additive mixed model.
Predictions are for eight hypothetical workers with different gender, smoking, and occupational (cotton vs. silk) exposures. Predictions assume that these workers have the same age, height, pack-year history (zero if non-smokers, the average number of pack-years if smokers) at each value of work cessation-years. Rug plot (bottom) indicates values of cessation-years for which an observation was present. No plateau is seen in FEV1 improvement after work cessation. For both men and women, FEV1 improvement is greatest in non-smoking silk > non-smoking cotton > smoking silk > smoking cotton workers.