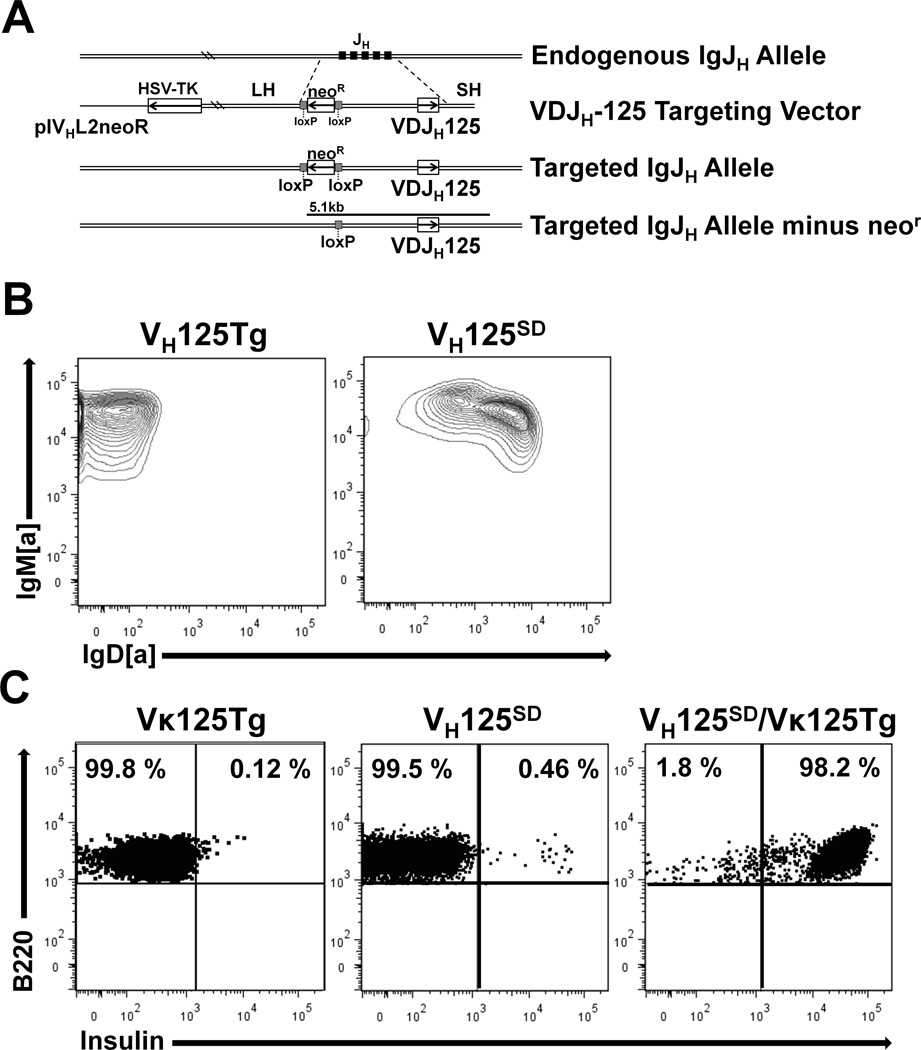
Figure 1. A site-directed BCR transgenic mouse model generates class switch-competent anti-insulin B lymphocytes.
(A) Strategy for targeting anti-insulin VDJH-125 to the Ig H chain locus (site-directed VH125SD). (B) Flow cytometry was used to assess IgM and IgD expression on B cells (B220+ live lymphocytes) from spleens of VH125SD B6 mice (right) and conventional IgM-restricted, non-site-directed VH125Tg B cells (left). (C) Insulin-binding B cells identified by flow cytometry in Vκ125Tg B6 mice (left), site-directed VH125SD B6 mice (middle), and in mice that harbor both VH125SD and Vκ125Tg (right).