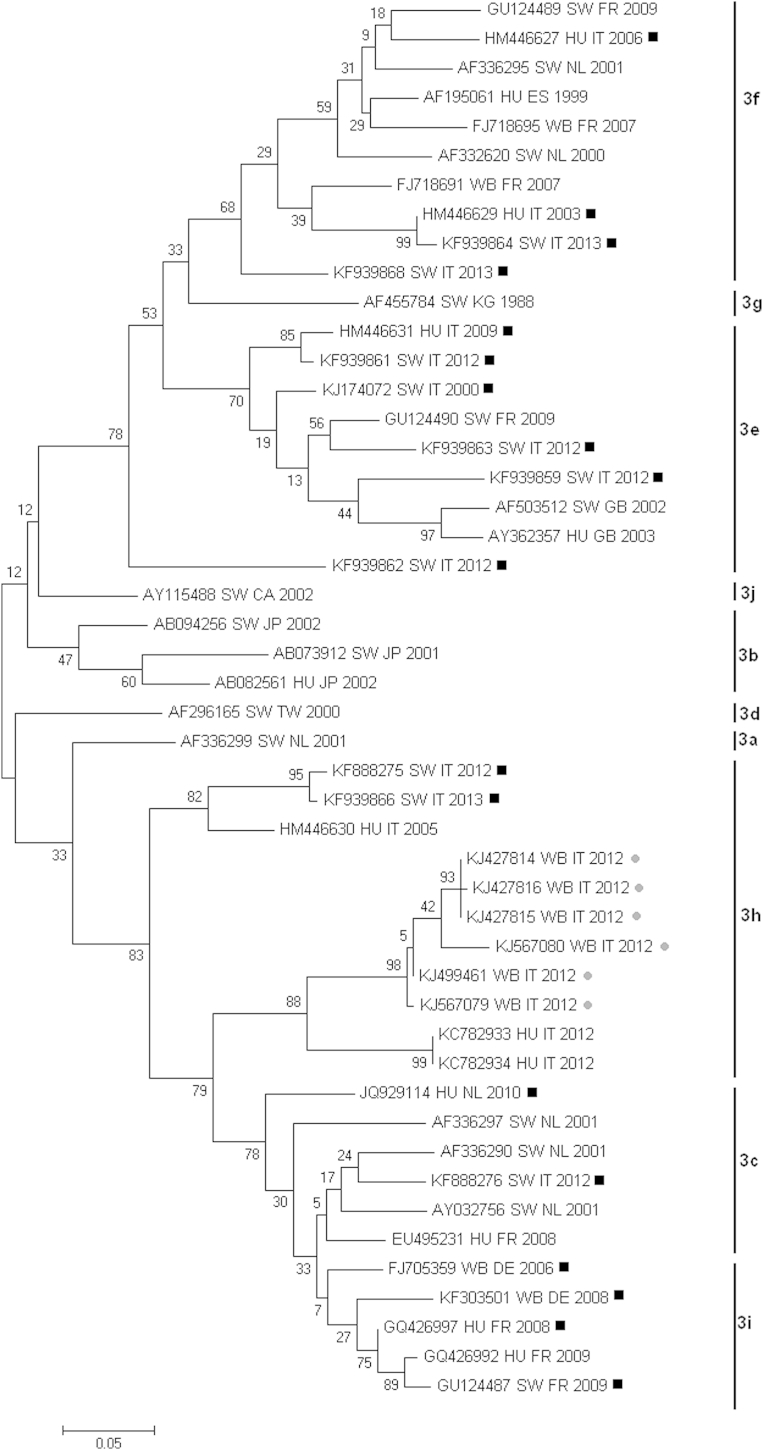
Fig. 2.
Molecular phylogenetic analysis by maximum-likelihood method. Phylogenetic tree on a set of ORF2 HEV genotype 3 sequences of human, wild boar and swine origin classified in subgroups. Evolutionary history was inferred by the maximum-likelihood method based on the Tamura-Nei model. The tree with the highest log likelihood (−3521.7122) is shown. The percentage of trees in which the associated taxa clustered together is shown next to the branches. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site. The analysis involved 48 nucleotide sequences. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA6 [21]. Black squares indicate assignment of putative subgroup; grey dots indicate wild boar–derived HEV sequences identified in this work. CA, Canada; CN, China; DE, Germany; EG, Egypt; ES, Spain; FR, France; GB, United Kingdom; HEV, hepatitis E virus; HU, human; IN, India; IT, Italy; JP, Japan; KG, Kyrgyzstan; MA, Morocco; MX, Mexico; NL, Netherlands; ORF, open reading frame; SW, swine; TD, Chad; TW, Taiwan; WB, wild boar.