Figure 4.
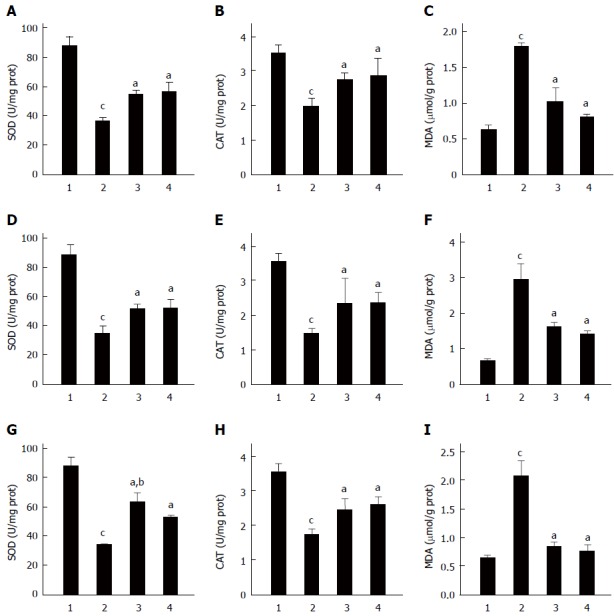
Effect of Clostridium butyricum on the activities of superoxide dismutase, catalase and the content of malondialdehyde in the gastric mucosa of mice with gastric ulcers induced by alcohol, cold stress or pylorus ligation. Gastric ulcer models were induced by alcohol (A-C), cold stress (D-F) or pylorus ligation (G-I), respectively. The activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) (A, D, G) and catalase (CAT) (B, E, H), and the content of malondialdehyde (MDA) (C, F, I) in the gastric tissues of different gastric ulcers (GU) mice were detected. For each GU model, there were four different groups: Sham control group (1), Model group (without pretreatment) (2), C. butyricum pretreatment group (3) and Omeprazole pretreatment group (4). The data were expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6). aP < 0.01 vs Model group; bP < 0.01 vs Omeprazole group; cP < 0.01 vs Sham control group.
