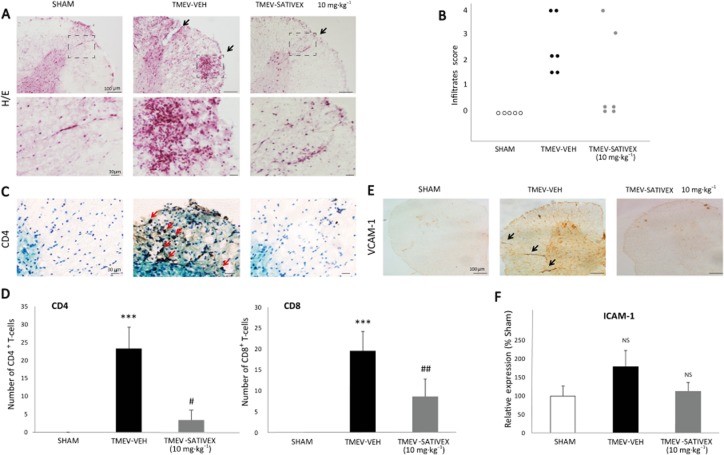
Figure 3.
A Sativex®-like phytocannabinoid combination treatment decreased leukocyte infiltration and down-regulated the adhesion molecules in the spinal cord of TMEV-infected animals. Transverse cervical spinal cord sections (30 μm thick) obtained at day 80 post-infection were stained with H&E (A). TMEV infection increased leukocyte infiltration, an effect that was attenuated by Sativex (10 mg·kg−1), as indicated by the infiltrate score (B) and by the analysis of CD4 and CD8 lymphocyte staining (representative microphotographs of CD4 staining, C; quantification of CD4 and CD8 number of positive cells, D). Sativex also showed a tendency to decrease mRNA expression of the ICAM-1 adhesion molecule as determined by RT-PCR on spinal cord of TMEV-infected animals (n = 6 per group) normalizing mRNA expression to that of the 18S gene, (F). Sativex significantly reduced the expression of VCAM-1 adhesion molecule (representative microphotographs of VCAM-1 staining, E). The data represent the mean ± SEM: ***P ≤ 0.001 versus Sham; #P ≤ 0.05, ##P ≤ 0.01 versus TMEV-VEH animals (non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test: CD4 and CD8 analysis). For histology analysis, five to six spinal cord slices per animal were analysed (n = 5–6 animals per group): Scale bar = 100 μm; 30 μm. NS, not significant.