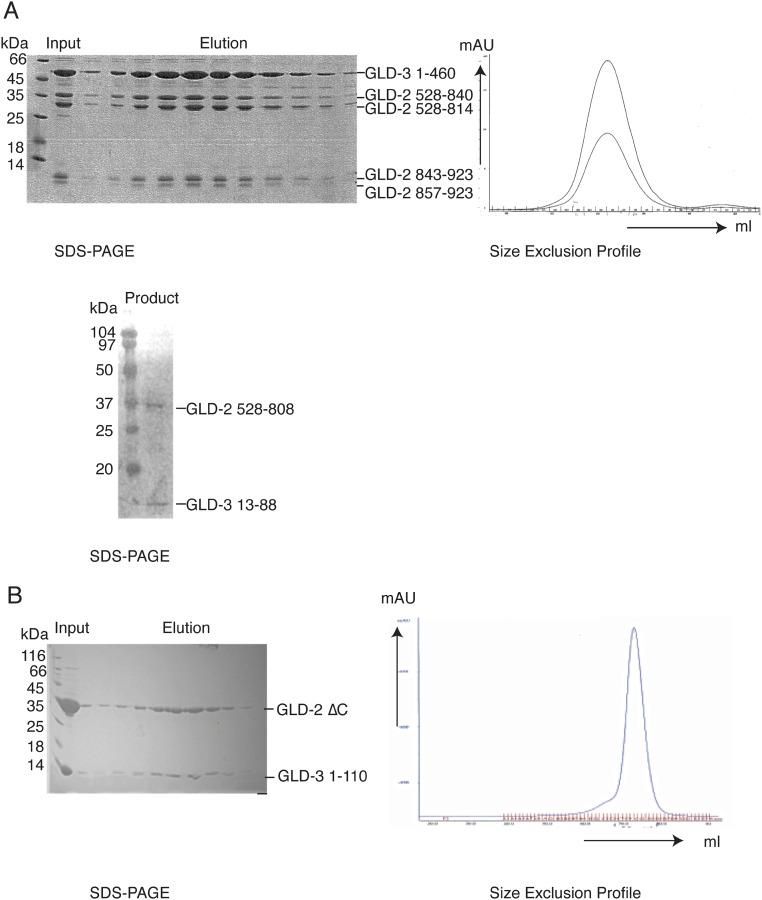
Fig. S1.
Biochemical characterization of the GLD-2–GLD-3 core complex. (A) Preparative and analytical limited proteolysis experiments. (Upper) Three milligrams of purified GLD-2528–1042–GLD-31–460 (34) was incubated with 90 μg of Elastase for 30 min on ice. The reaction was stopped by adding 1:10 (vol/vol) AEBSF (150 mM) and loaded on a gel filtration column (Superdex 200; GE Healthcare). Using mass spectrometry and N-terminal sequencing analyzes, we mapped the domain boundaries of GLD-2528–1042 to a smaller core domain, GLD-2528–923, whereas GLD-31–460 was not affected by elastase. The chromatography profile is shown at Right, and the Coomassie-stained 15% SDS/PAGE is shown at Left. (Lower) Ten microliters of purified GLD-2528–808–GLD-31–106 (1 mg/mL) was incubated with 3 μL of GluC (0.1 mg/mL) and incubated for 30 min on ice. The reaction was stopped by the addition of 5 μL of SDS loading dye. For this complex, we identified proteolytically sensitive regions at GLD-3 residues 1–12 and 89–106 (34), whereas GLD-2528–808 was not affected by GluC. Shown is the Coomassie-stained 15% SDS/PAGE of the complex after proteolysis. (B) Purification of GLD-2ΔC–GLD-31–110. The protein complex was expressed and purified as described in the method section. The Coomassie-stained 15% SDS/PAGE of the protein complex after size exclusion is shown at Left. The respective size exclusion profile is shown at Right (blue line: UV280).