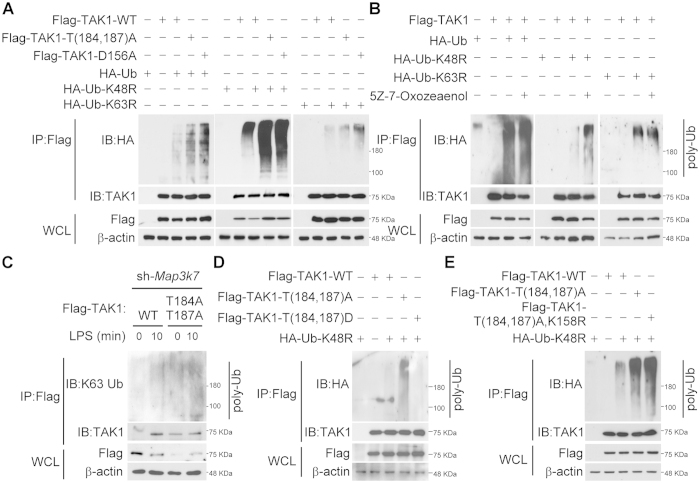
Figure 2. Lys63-linked polyubiquitination of TAK1 is enhanced by blocking TAK1 phosphorylation.
A, TAK1 polyubiquitnation is enhanced by blocking TAK1 phosphorylation. Flag-tagged TAK1 wild-type (WT), T(184,187)A, or D156A mutants were co-expressed in HEK293T cells with HA-tagged Ub WT, K48R, or K63R mutants. The cells were lysed, immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody, extensively washed, and gel separated. Polyubiquitination was detected with anti-HA antibody. B, TAK1 polyubiquitination is enhanced by inhibiting TAK1 activation. Flag-tagged WT TAK1 was co-expressed in HEK293T cells with HA-tagged Ub WT, K48R, or K63R mutants. After treatment with TAK1 inhibitor 5Z-7-oxozeanenol (100 nM) for 30 min, the cells were lysed, immunoprecipitated, and ubiquitination was detected with anti-HA antibody. C, in response to LPS, TAK1 polyubiquitnation is enhanced in TAK1 T(184,187)A mutant. TAK1-silenced RAW264.7 cells were reconstituted with Flag-tagged TAK1 wild-type (WT) or T(184,187)A mutant. The cells were incubated with LPS for the indicated times, lysed, immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody, extensively washed, and gel separated. Polyubiquitination was detected with anti-Lys63-linked Ub antibodies. D, non-Lys48-linked polyubiquitination of TAK1 is blocked by TAK1 phosphorylation. Flag-tagged TAK1 wild-type (WT), T(184,187)A, or T(184,187)D mutants were co-expressed in HEK293T cells with HA-tagged K48R Ub mutant. The cells were collected, and analyzed using in vivo ubiquitination assay. E, enhancement of TAK1 polyubiquitination induced by TAK1 inhibition is not at the Lys158 residue. Flag-tagged TAK1 wild-type (WT), T(184,187)A, or T(184,187)A, K158R mutants were co-expressed in HEK293T cells with HA-tagged Ub K48R mutant. The cells were collected and analyzed for polyubiquitination. The result are represented from at least three independent experiments.