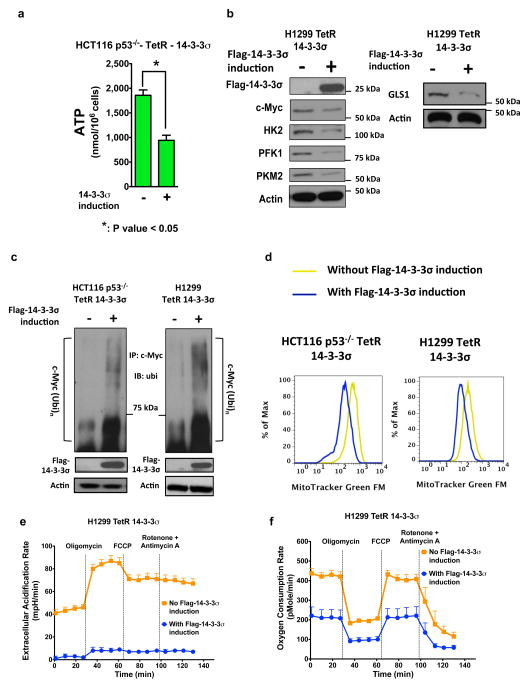
Figure 7. 14-3-3σ effectively suppresses metabolic reprogramming in p53-deficient colorectal and lung cancer cells.
(a) 14-3-3σ expression decreased energy production in p53-deficient colorectal carcinoma cells. ATP measurements were shown. Bars represent means ± 95% CI; Student t-test, * p < 0.05
(b) 14-3-3σ reduced expression of c-Myc as well as c-Myc glycolytic and glutaminolytic targets in p53-null H1299 lung cancer cells. Flag-14-3-3σ expression was induced in the cells. c-Myc, HK2, PFK1, PKM2, and GLS1 protein levels of induced and non-induced H1299 cells were compared.
(c) 14-3-3σ promoted c-Myc polyubiquitination in p53-deficient cancer cells. Flag-14-3-3σ expression was induced in indicated cells (+). Non-induced cells were used as a control (−). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-c-Myc antibodies and immunoblotted with anti-ubiquitin (ubi) antibodies.
(d) Induction of 14-3-3σ expression reduced mitochondrial mass of p53-null cancer cells. Mitochondria of HCT116 p53−/− TetR 14-3-3σ and H1299 TetR 14-3-3σ cells were stained with MitoTracker Green FM.
(e) 14-3-3σ reduced extracellular acidification rate of p53-null H1299 cells. Extracellular acidification rate (ECARs), which reflects glycolytic activity, was measured in induced and non-induced H1299 TetR 14-3-3σ cells.
(f) 14-3-3σ suppressed oxygen consumption and mitochondrial respiration in p53-deficient cells. Oxygen consumption and mitochondrial respiration of induced and non-induced H1299 TetR 14-3-3σ were measured.