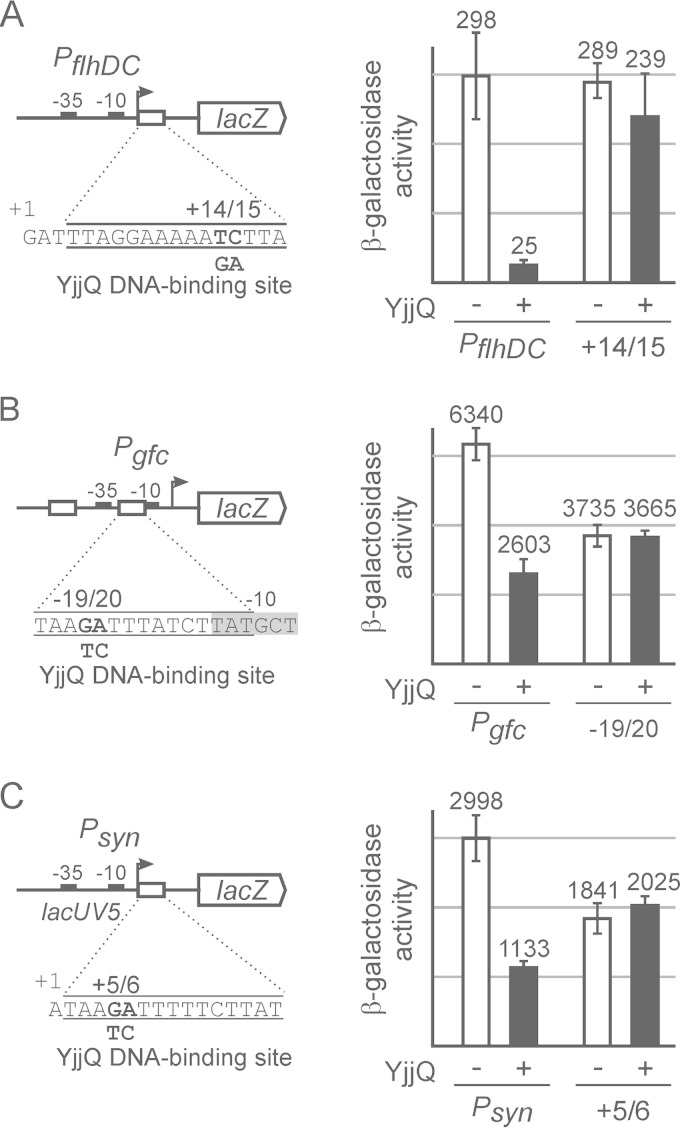
FIG 2.
Mutation of the putative YjjQ DNA-binding site abrogates repression by YjjQ. Promoter-lacZ fusions and their mutant derivatives carrying mutations in the putative YjjQ DNA-binding site were integrated in strain T23. The expression level was determined for transformants of these reporter strains with control plasmid pKESK22 (−) and yjjQ-containing plasmid pKEKD31 in the presence of YjjQ (+). Schematically shown are the main features of the promoter-lacZ fusions, such as the transcription start site (+1), the −10 and the −35 boxes, as well as the sequences of the putative YjjQ DNA-binding sites and the mutations that were introduced. Tested were the flhDC promoter (PflhDC) (strain T1266) and its mutant derivative (+14/15) carrying a 2-nucleotide exchange at positions +14 and +15 relative to the transcription start (strain T1661) (A), the gfc promoter (Pgfc) (strain 1541) and its mutant derivative (−19/20 [strain T1664]) (B), and a synthetic promoter consisting of the lacUV5 core promoter and the YjjQ DNA-binding motif fused immediately downstream of the transcription initiation site (strain T1675), as well as its mutant derivative (+5/6 [strain T1667]) (C). Transformants of these reporter strains with the control plasmid pKESK22 (− YjjQ) and with plasmid pKEKD31 (+ YjjQ) were grown to an OD600 of 0.5 in LB medium supplemented with kanamycin and IPTG. Given is the average of enzyme activities determined from at least 3 independent biological replicates.