Figure 3. Summary of melanoma risk with melanin types and its potential link with neurodegenerative diseases.
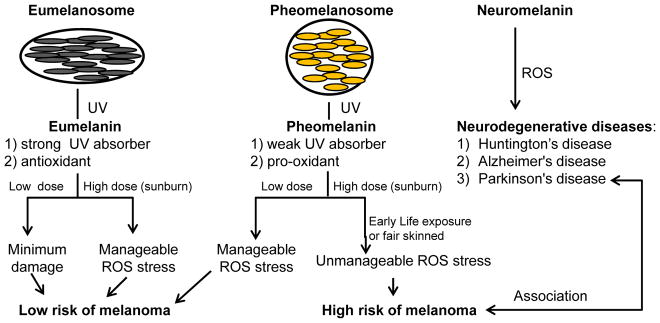
Eumelanin strongly absorbs UV radiation and serves as an antioxidant, hence in dark skinned individuals the UV/ROS induced stress is well managed and melanomas are rare. In pheomelanin-predominant light skinned individuals, pheomelanin does not efficiently absorb UV radiation, and upon UV radiation pheomelanin becomes a pro-oxidant. Hence, with high UV doses the stress is difficult to manage and melanoma risk increases greatly in these individuals. A potential link of UV/ROS-induced amyloid toxicity is suggested by the shared risk of some individuals for cutaneous melanoma and Parkinson’s disease.
